Hadoop 教程 | InputFormat相关逻辑整理
Hadoop MapReduce 任务读取主要是通过 InputFormat 类来完成的, 他主要的功能是将要读取的文件集合切分成多个分片,每一个分片对应一个数据读取任务。
当任务开始运行时,每个任务依次遍历迭代获取一条有效记录,以此来将数据读取完成。
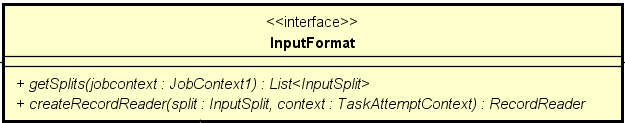
getSplits(jubContext:JobContext):List<InputSplit> 的主要作用是获取任务要读取文件的所有的分片集合,这里每一个 InputSplit 对应一个读任务。
任务起来以后通过 createRecordReader(split:InputSplit, context:TaskAttemptContext):RecordReader 创建一个数据读写工具
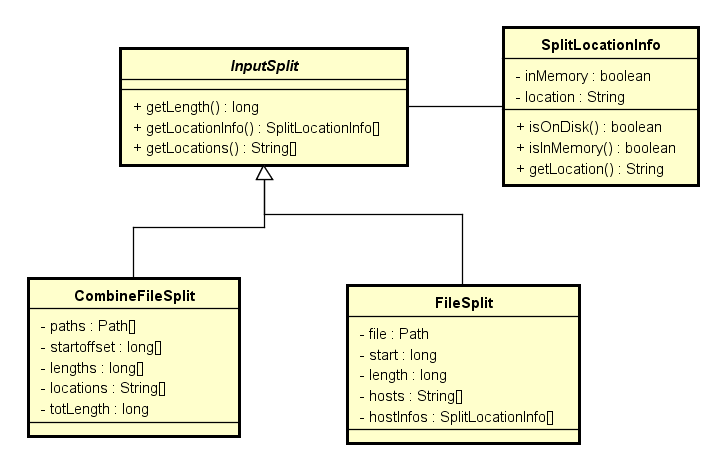
InputSplit
InputSplit 主要来记录要读取分片的相关元信息, 比如最常用的 FileSplit 与 CombineFileSplit,主要用来记录文件分片的位置,起始偏移,读取记录长度等信息。
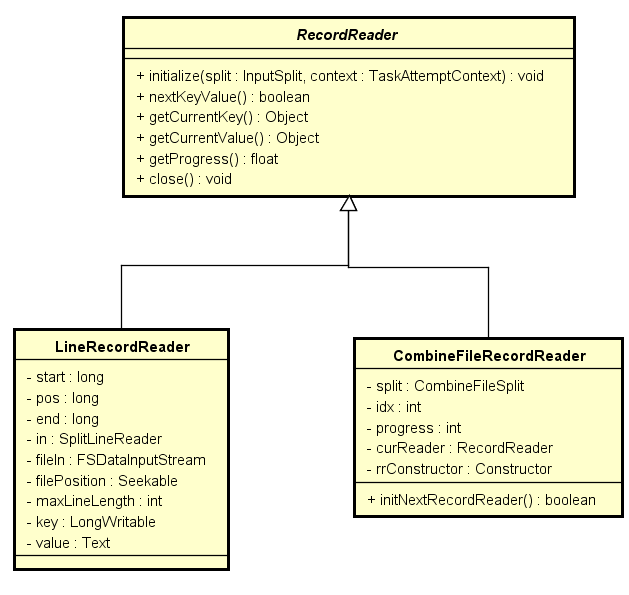
RecordReader
RecordReader主要功能是基于当前InputSplit 来获取数据内容,通过 nextKeyValue 来循环迭代获取数据。其使用方式如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
recordReader = RecordReader(...)
recordReader.initizlize(split, jobContext) // 初始化当前的 RecordReader
while(recordReader.nextKeyValue()){
key = recordReader.getCurrentKey()
value = recordReader.getCurrentValue()
}
recordReader.close()
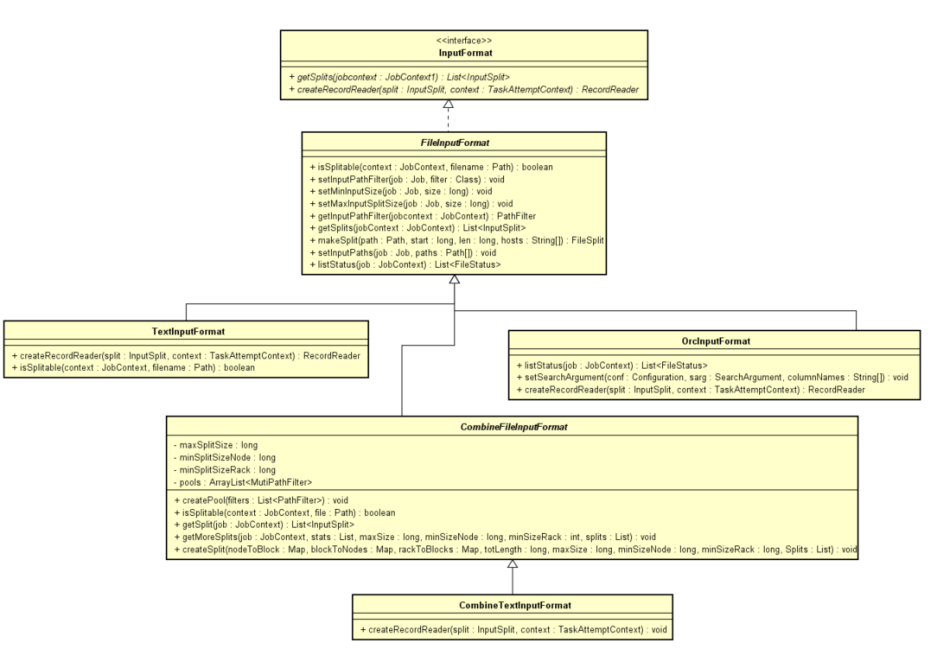
InputFormat
InputFormat 使用较多的是 FileInputFormat 及其派生类, 它的主要功能逻辑是 :
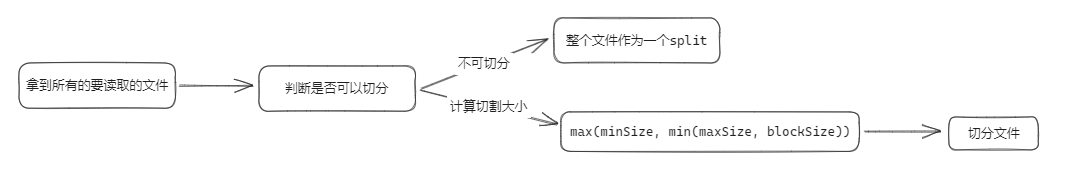
- 获取要读取的文件 :
listStatus() - 判断文件是否可以切割 :
isSplitable() - 按照具体的逻辑切分文件组织成
InputSplit
listStatus
FileInputFormat 的族系中基本都是沿用了 FileInputFormat 中的 listStatus() 来获取要读取的文件集合。
用户可以使用 mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.list-status.num-threads 选项来配置解析的线程数量
首先通过读取
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.inputdir配置,来拿到所有输入路径遍历所有的路径,遍历过程用户支持自定义路径过滤规则,默认情况下过滤 以
.开头,或者_开头的文件或目录:a. 将所有的匹配到所有所有文件放入读取文件集合中
b. 如果是目录,则遍历目录下面的所有文件,加入到读取文件集合中
c. 如果下一层还是目录,则
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.input.dir.recursive选项控制,是否进行递归读取,否则忽略二级目录。
isSplitable
是否可切分在不同存储类型中是不同的
常见的 ORCInputFormat, ParquetInputFormat, SequenceFileInputFormat 是支持切分的
TextInputFormat, CombineTextInputFormat 是否支持切分得看它的压缩类型,无压缩类型与bz压缩是支持split 的, 其他不支持。
FileInputFomat 文件切分逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Path path = file.getPath(); // 文件路径
long length = file.getLen(); // 文件大小
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize(); // 获取文件块大小
// max(minSize, min(maxSize, blockSize))
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize); // 计算读取的块大小
long bytesRemaining = length;
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
// 起始位置 : length - bytesRemining
// 长度 : splitSize
// 文件位置 : path
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(), blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
}
CombineFileInputFomat 文件切分逻辑
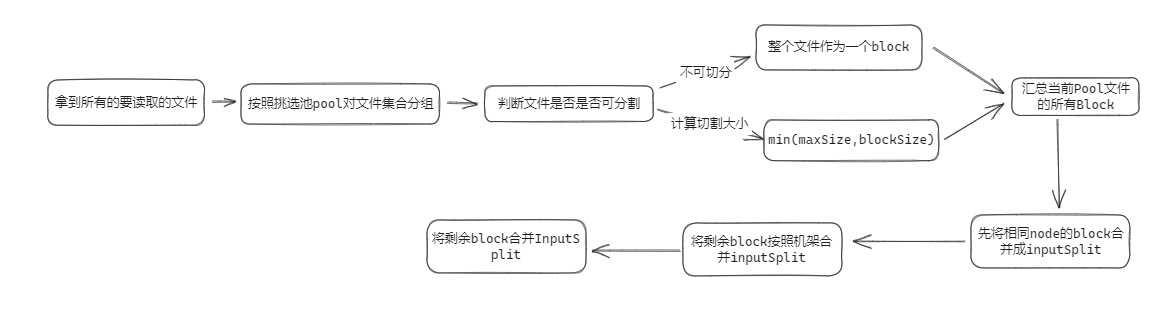
CombineFileInputFormat 与 FileInputFormat 的区别就是 CombineFileInputFormat 能够支持跨文件的 InputSplit
它的具体步骤为 :
文件切分成Block的步骤:
获取这个文件的所有的
BlockLocation:fs.getFileBlockLocations(stat, 0, stat.getLen())基于每个
BlockLocation判断其最终产生的Block :min(maxSize, blockSize)
Block集合合并成InputSplit:
在Split 过程中,它优先将同一个host的Block进行合并成
InputSplit,需要a. 每个Node级别
InputSplit的Block集合大小不能超过maxSizeb. 如果当前host的所有Block大小不足
maxSize, 但是超过minSizeNode,则将所有的Block合并成一个InputSplitc. 如果以上都不满足的Block集,则进入机架合并策略
如果同一个host的Block总大小太小,不足以合并成一个
InputSplit, 那么就放宽条件,尝试合并同一个机架的 Blocka. 每个机架级别
InputSplit的Block集合大小不能超过maxSizeb. 如果当前机架的所有Block大小不足
maxSize, 但是超过minSizeRack,则将所有的Block合并成一个InputSplitc. 如果以上都不满足的Block集,则进入机架合并策略
如果仍然有部分Block不满足上面的条件,则将剩余Block统一放在一个集合中,按照maxSize切分
参数说明
FileInputFormat
| 参数名 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize | 文件分割时最小的的split |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize | 文件分割时最大的split |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.inputdir | 文件的读取路径 |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.input.dir.recursive | 是否递归遍历 |
mapreduce.input.pathFilter.class | 指定文件过滤类 |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.list-status.num-threads | 读取文件需要的线程数 |
CombineFileInuptFormat
| 参数名 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize.per.node | 节点级别可以合并的最小分片大小 |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize.per.rack | 机架级别可以合并的最小分片大小 |
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize | 最大分片大小 |