Leveldb 教程 | Leveldb 数据写入流程
LevelDB 数据插入大致分成两个阶段: 写内存,写磁盘
- 用户当前插入的数据会被记录在MemTable中,这是一个基于内存的数据查询引擎。
- 当MemTable中数据插入超过一定的容量后,此时会重新开一个MemTable, 用于应对客户端的写请求。
- 写满的MemTable将会被异步刷盘,形成SSTable.
key细节部分
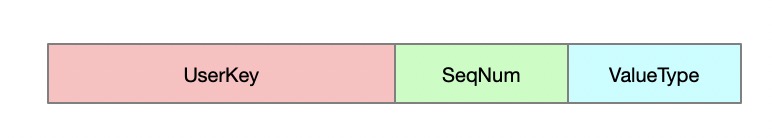
用户提交的key(UserKey)在leveldb内部会被转换成 InternalKey。
InternalKey 组成部分 :
UserKey: 用户提交的keySequenceNumber: 8个字节,从1自增得到的序列码ValueType: 1个字节,表示数据的类型, 插入操作(0x1), 删除操作(0x0)
InternalKey := concat(UserKey, uint64_t(SequenceNumber<<8 | ValueType))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
/***
* InternalKey 的封装结构
*/
struct ParsedInternalKey {
Slice user_key; // 用户提交的 key
SequenceNumber sequence; // 序列编码
ValueType type; // 数据操作类型
ParsedInternalKey() {} // Intentionally left uninitialized (for speed)
ParsedInternalKey(const Slice& u, const SequenceNumber& seq, ValueType t)
: user_key(u), sequence(seq), type(t) {}
std::string DebugString() const;
};
/****
* 合并 SequenceNumber 与 ValueType
*/
static uint64_t PackSequenceAndType(uint64_t seq, ValueType t) {
assert(seq <= kMaxSequenceNumber);
assert(t <= kValueTypeForSeek);
return (seq << 8) | t;
}
void AppendInternalKey(std::string* result, const ParsedInternalKey& key) {
result->append(key.user_key.data(), key.user_key.size()); // 首先存入 user key
PutFixed64(result, PackSequenceAndType(key.sequence, key.type)); // 最后64位填充 sequence+type
}
/***
* InternalKey 构造函数
*/
InternalKey(const Slice& user_key, SequenceNumber s, ValueType t) {
AppendInternalKey(&rep_, ParsedInternalKey(user_key, s, t));
}
SequenceNumber
在leveldb中,使用SequenceNumber主要用来支持多版本数据, 同一个key(UserKey)可能被插入多次。
在系统内部,多次插入的key将使用不同的SequenceNumber标记,越晚插入的keySequenceNumber越大,表示数据越新。
在查询时,优先会查到最大SequenceNumber的key(即最晚插入), 以此实现upsert.
在后期Compaction过程中, 多版本的UserKey会被合并,只保留最大的SequenceNumber数据。
ValueType
因为leveldb不能实时的在物理上删除数据,所以提供了 ValueType 标志位,用来标志这条数据是否有效。
当ValueType标志位设置0x1时,表示此数据有效。 当ValueType标志位设置0x0时,表示此数据无效即被删除。
InternalKey 排序
InternalKey在MemTable与SST中的排序方式相同,按照从小到大的key有序。
因为key的有序性,所以在查找时多采用二分查找的方式,找到第一个大于等于目标key的数据。
InternalKeyComparator比较器在这里起着重要作用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
class BytewiseComparatorImpl : public Comparator {
public:
BytewiseComparatorImpl() = default;
....
// 实现的比较方式
int Compare(const Slice& a, const Slice& b) const override {
return a.compare(b);
}
....
}
class InternalKeyComparator : public Comparator {
。。。
int Compare(const Slice& a, const Slice& b) const const {
// 首先比较 user_key
// 此处的 user_comparator_ 为 BytewiseComparatorImpl 实现的比较器
int r = user_comparator_->Compare(ExtractUserKey(akey), ExtractUserKey(bkey));
// 如果 user_key 相同, 则比较其版本
// 这个地方发生了改变,版本越大的比较得到的结果越小
// 这样在排序的时候,就会把大版本的同一个key放到比较靠前的地方去
if (r == 0) {
const uint64_t anum = DecodeFixed64(akey.data() + akey.size() - 8); // 获取版本号
const uint64_t bnum = DecodeFixed64(bkey.data() + bkey.size() - 8); // 获取版本号
if (anum > bnum) {
r = -1;
} else if (anum < bnum) {
r = +1;
}
}
return r;
};
。。。
};
从上面可以看出, InternalKeyComparator在处理key大小时做了特殊处理:
- 如果user_key不相同,则直接采用
std::string.compare的方式比较。 - 如果user_key相同,则效果与
std::string.compare相反, 序列号越大的值越小,这样排序后越靠前。
1
2
3
比如插入数据key依次为 : a(1),b(2),a(3),c(4)
则存储顺序依次为 : | a_3 | a_1 | b_2 | c_4 |
采用这种方式使得在数据查找时可以使用二分查找时更快的找到数据,并且优先查到有效数据。
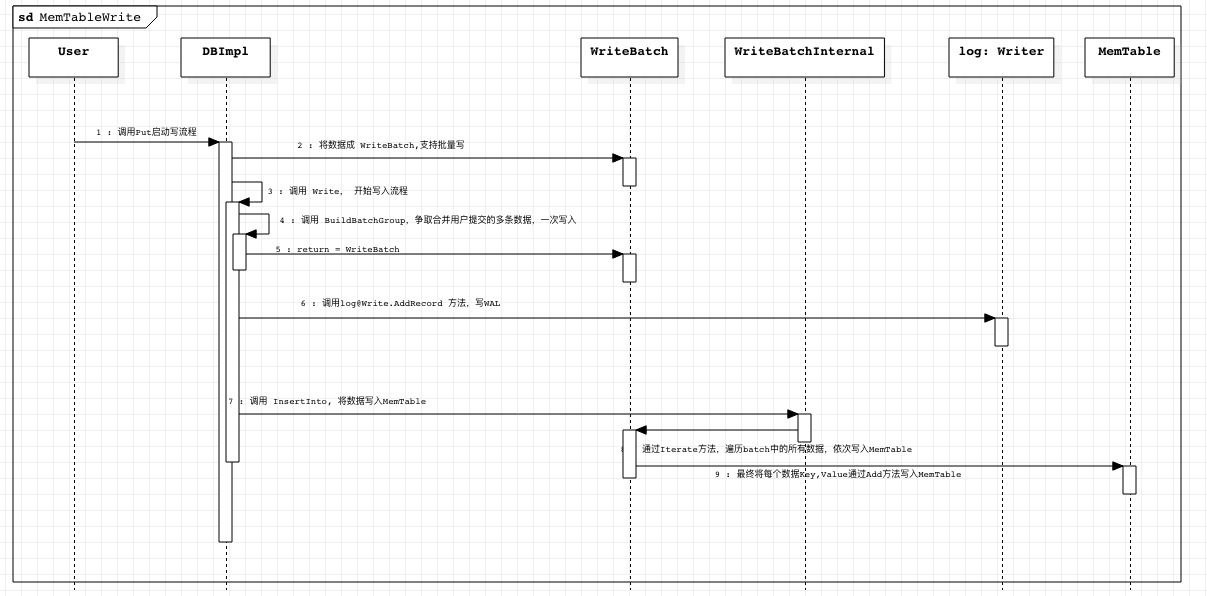
数据写内存
数据写内存过程主要将数据写到 MemTable
说明
- 数据写入之前会首先写 WAL, 用于数据的恢复。
- 数据的写入过程借助了 WriteBatch, 其目的是对应于多线程写数据的场景,借助 WriteBatch争取一次将更多的写入请求合并写给 MemTable.
WriteBatch
WriteBatch 是一个可以维护多个Entry的数据结构,这里Entry指代需要插入或者删除的数据。
- 对于插入数据,
Entry包含要插入的数据的key+value内容。 - 对于删除数据,
Entry只包含了要删除数据的key。
其数据结构为 :
- SequenceNumber : 要插入的第一个
Entry的序列号, 后面的依顺序自增1。 - entry_count : 这个WriteBatch包含的
Entry数目 - Entry:要插入或者删除的数据内容
基本的操作类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
## from write_batch.cc
std::string rep_; // WriteBatch 具体数据存储
/***
* 将 value 的长度与value 填充到dst
*/
void PutLengthPrefixedSlice(std::string* dst, const Slice& value) {
PutVarint32(dst, value.size()); // 填充 value 长度
dst->append(value.data(), value.size()); // 填充 value 数据
}
/***
* 获取WriteBatch中元素的数量
*/
int WriteBatchInternal::Count(const WriteBatch* b) {
return DecodeFixed32(b->rep_.data() + 8);
}
/***
* 设置 WriteBatch 中元素的数量
*/
void WriteBatchInternal::SetCount(WriteBatch* b, int n) {
EncodeFixed32(&b->rep_[8], n);
}
/***
* 获取 WriteBatch 的 SeqNum
*/
SequenceNumber WriteBatchInternal::Sequence(const WriteBatch* b) {
return SequenceNumber(DecodeFixed64(b->rep_.data()));
}
/***
* 设置 SeqNum
*/
void WriteBatchInternal::SetSequence(WriteBatch* b, SequenceNumber seq) {
EncodeFixed64(&b->rep_[0], seq);
}
/***
* 插入一个KeyValue 到WriteBatch中
*/
void WriteBatch::Put(const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
// 更新 Header 中关于元素数量部分
// 增一操作
WriteBatchInternal::SetCount(this, WriteBatchInternal::Count(this) + 1);
// 设置数据类型为 : kTypeValue(插入操作)
rep_.push_back(static_cast<char>(kTypeValue));
// 填充数据
PutLengthPrefixedSlice(&rep_, key);
PutLengthPrefixedSlice(&rep_, value);
}
/***
* 通过追加写的方式删除一个Key在WriteBatch中
*/
void WriteBatch::Delete(const Slice& key) {
WriteBatchInternal::SetCount(this, WriteBatchInternal::Count(this) + 1);
rep_.push_back(static_cast<char>(kTypeDeletion));
PutLengthPrefixedSlice(&rep_, key);
}
MemTable
MemTable 为内存数据的查询引擎,它主要保存最新的写入数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
class MemTable {
public:
// 构造器
explicit MemTable(const InternalKeyComparator& comparator);
MemTable(const MemTable&) = delete;
MemTable& operator=(const MemTable&) = delete;
// 增加一个外部引用
void Ref() { ++refs_; }
// 释放引用
// 如果外部无引用, 则释放存储
void Unref() {
--refs_;
assert(refs_ >= 0);
if (refs_ <= 0) {
delete this;
}
}
// 返回容量大小 arena_.MemoryUsage()
size_t ApproximateMemoryUsage();
// 返回迭代器 MemTableIterator
Iterator* NewIterator();
/***
* 添加一个 kv 数据到 memtable 中
* @param seq seqnum 唯一标识这个kv的序列号
* @param type 存储类型 kTypeDeletion(删除操作), kTypeValue(插入操作)
* @param key 数据实体 key
* @param value 数据实体 value
*/
void Add(SequenceNumber seq, ValueType type, const Slice& key, const Slice& value);
// 从MemTable中查询数据
bool Get(const LookupKey& key, std::string* value, Status* s);
private:
friend class MemTableIterator;
friend class MemTableBackwardIterator;
// InternalKey 比较器
struct KeyComparator {
const InternalKeyComparator comparator;
explicit KeyComparator(const InternalKeyComparator& c) : comparator(c) {}
int operator()(const char* a, const char* b) const;
};
typedef SkipList<const char*, KeyComparator> Table; // 数据体, 使用跳表维护
~MemTable(); // Private since only Unref() should be used to delete it
KeyComparator comparator_; // key 比较器
int refs_;
Arena arena_; // 内存池工具
// 跳表结构实现
Table table_;
};
MemTable 主要是用了内存池Arena与跳表SkipList技术实现。
Arena: 内存池技术,防止频繁的申请资源。SkipList: 用于数据维护与快速数据索引,对于数据查询类似于二分查找。
每一个数据在MemTable中的数据结构为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// memtable.cc
/**
* <pre>
* 将用户提交的的KeyValue插入到MemTable中
* </pre>
* @param s seqnumber
* @param type ValueType
* @param key UserKey
* @param value value 数据, 对于delete事件, value 为空
*/
void MemTable::Add(SequenceNumber s, ValueType type, const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
size_t key_size = key.size(); // user_key
size_t val_size = value.size(); // value
size_t internal_key_size = key_size + 8; // internal_key size
// 从内存池中分配内存: key_size | internel_key | value_size | value
const size_t encoded_len = VarintLength(internal_key_size) + internal_key_size + VarintLength(val_size) + val_size;
char* buf = arena_.Allocate(encoded_len);
// 填充 key_size
char* p = EncodeVarint32(buf, internal_key_size);
// 填充 InternalKey
std::memcpy(p, key.data(), key_size);
p += key_size;
EncodeFixed64(p, (s << 8) | type);
p += 8;
// 填充 value_size
p = EncodeVarint32(p, val_size);
// 填充 value
std::memcpy(p, value.data(), val_size);
assert(p + val_size == buf + encoded_len);
// 数据插入到 memtable 中
table_.Insert(buf);
}
它在SkipList主要使用InternalKey来比较排序数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// 从MemTable插入到跳表的元素中取出InternalKey
static Slice GetLengthPrefixedSlice(const char* data) {
uint32_t len;
const char* p = data;
p = GetVarint32Ptr(p, p + 5, &len); // +5: we assume "p" is not corrupted
return Slice(p, len);
}
/***
* memtable key 比较器
*/
int MemTable::KeyComparator::operator()(const char* aptr,
const char* bptr) const {
Slice a = GetLengthPrefixedSlice(aptr); // 从数据中提取 key
Slice b = GetLengthPrefixedSlice(bptr);
return comparator.Compare(a, b);
}
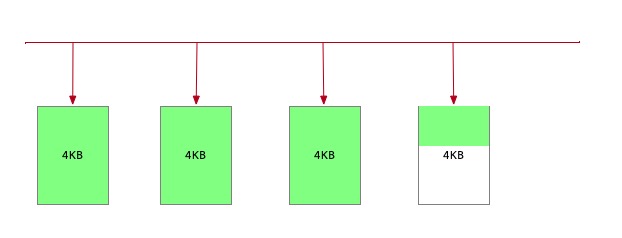
Arena 内存池
为了避免频繁的new内存操作, Leveldb在MemTable使用了内存池的技巧。
Arena每次开辟一个Block(4KB)为上层提供存储空间。每当上层想要申请一块资源时,便从开辟的这个Block划分出一块提供服务,如果剩余空间不足以满足用于请求,则重新开辟一个Block用于服务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
// arena.h arena.cc
// 分配指定数量的内存大小
// 如果当前的内存块满足申请需求,则从当前的内存块中取出一部分内存分配给用户
// 如果当前的内存块剩余内存不满足用户申请,则调用 AllocateFallback 为用户请求一块内存
// -- 在这里,如果是申请的内存大于 1024KB, 则认为是申请的大内存, 则为其单独申请一块内存, 当前的block 仍然可以为后续内存请求分配内存
// -- 如果申请的内存不足 1024KB, 则认为当前的block 剩余的内存资源太少(内存碎片),不足以满足用户后续的多数请求, 则重新分配一个block, 为用户提供内存分配需要
inline char* Arena::Allocate(size_t bytes) {
assert(bytes > 0);
if (bytes <= alloc_bytes_remaining_) {
char* result = alloc_ptr_;
alloc_ptr_ += bytes;
alloc_bytes_remaining_ -= bytes;
return result;
}
return AllocateFallback(bytes);
}
char* Arena::AllocateAligned(size_t bytes) {
// 可以说是用来判断当前 cpu 地址宽度
const int align = (sizeof(void*) > 8) ? sizeof(void*) : 8;
// 地址宽度必须是 2 的指数倍
static_assert((align & (align - 1)) == 0, "Pointer size should be a power of 2");
// 将指针转为整数
// 用来判断当前还差内存才会对齐
size_t current_mod = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(alloc_ptr_) & (align - 1);
size_t slop = (current_mod == 0 ? 0 : align - current_mod);
size_t needed = bytes + slop;
char* result;
if (needed <= alloc_bytes_remaining_) {
// 内存先对齐
result = alloc_ptr_ + slop;
alloc_ptr_ += needed;
alloc_bytes_remaining_ -= needed;
} else {
// AllocateFallback always returned aligned memory
result = AllocateFallback(bytes);
}
// 判断系统分配的内存是否对齐
assert((reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(result) & (align - 1)) == 0);
return result;
}
// 资源不足时重新分配资源
char* Arena::AllocateFallback(size_t bytes) {
if (bytes > kBlockSize / 4) {
// 如果申请的内存大于 1/4 block_size
// 直接分配一个 大小为 bytes 的内存块
char* result = AllocateNewBlock(bytes);
return result;
}
// 如果申请的内存不足 1/4 的内存块
// 则申请一个4KB 的内存块
// 然后将这个内存块的一部分分配给用户,然后记录剩余部分的位置与大小
alloc_ptr_ = AllocateNewBlock(kBlockSize);
alloc_bytes_remaining_ = kBlockSize;
char* result = alloc_ptr_;
alloc_ptr_ += bytes;
alloc_bytes_remaining_ -= bytes;
return result;
}
// 向系统申请一个大小为 block_bytes 的内存块挂到 blocks_
char* Arena::AllocateNewBlock(size_t block_bytes) {
char* result = new char[block_bytes];
blocks_.push_back(result);
memory_usage_.fetch_add(block_bytes + sizeof(char*),
std::memory_order_relaxed);
return result;
}
在此基础上, Arena 为上层提供了两个接口 :
Allocate: 为上层提供普通的内存空间AllocateAligned: 为上层提供从对齐地址开始的内存空间
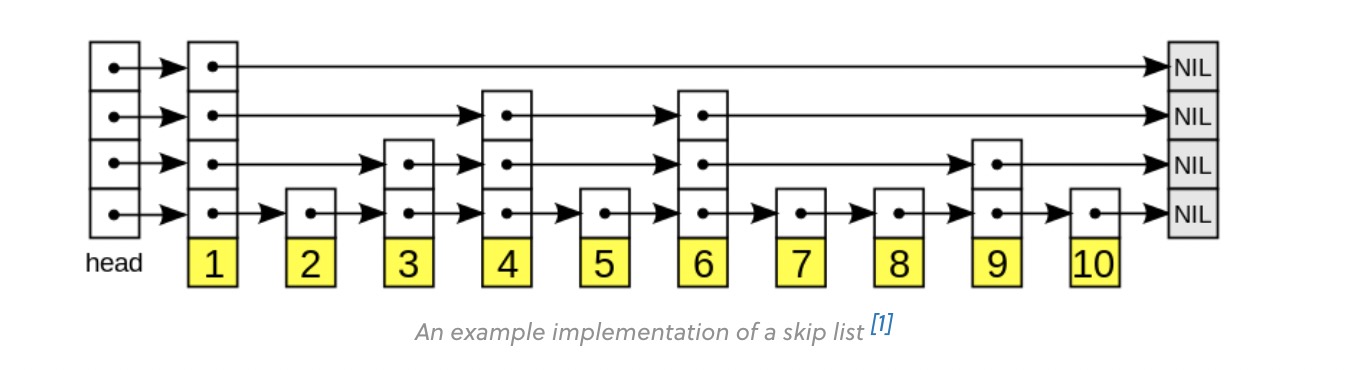
SkipList
SkipList 是一个用于快速索引数据的数据结构,其内部使用了多级链表的实现方式。
它相对于常见的二叉查找树在实现上逻辑更加简单,而且性能较好。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// 调表节点结构
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node {
Key const key;
// 指向后面节点的调表
// 数组长度不固定,动态分配
// next_[0] 是最低级的链表
std::atomic<Node*> next_[1];
};
SkipList本身属于一个有序链表,它从前往后的值依次递增,他与单层链表的区别是,他的每一个节点有多个指针(最高12)。
从 next_[0] ~ next_[11] 层级越高他的跨度越大,而且不是每一个节点都有12层指针。层数越高,含有该层的节点越少。
SkipList 查找过程是类似于二分查找 :
- 从head处出发, 从高的level指针开始查找,如果
next_[level]为空或者next_[level]的值大于等于要比较的值,则降低level进行查询。 - 降低
level相当于缩短步长,在小步长内缩短范围查找,超找方式依旧如上。 - 直到
level==0。此时他的next_[0]要么是目标数据,要么目标数据不在这个SkipList中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// skiplist.h
/****
* 找到大于等于目标数据的节点数据
*
* @param key 查找的目标数据
* @param prev 如果key为带插入目标数据,prev记录从0-11层,所有待插入节点的前序节点
*/
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev) const {
// 从头部开始遍历
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) { // 判断key是否比下一个节点数据大
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x; //
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
level--;
}
}
}
}
SkipList插入节点时利用FindGreaterOrEqual找到所有前序节点。此时在随机生成一个level(level越大生成的概率越低)。然后将0~(level-1)层指针加入到SkipList中,完成链表扩展。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// 重点内容 :
// 填充一个元素到跳表结构中
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
Node* prev[kMaxHeight]; // pre 是一个未初始化的指针
// 利用FindGreaterOrEqual找到所有的前向节点
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
int height = RandomHeight(); // 生成一个随机高度
// 如果深度超过了当前最高的跳表指针深度,则需要将头部node指向改新node
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
// 节点插入列表
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
数据写磁盘
当MemTable容量超过限制(options_.write_buffer_size参数控制, 默认4MB), levelDB 会新建一个MemTable用于处理用户提交的写请求。
而这个MemTable将会被刷到磁盘形成SST 文件。
MemTable的数据落盘主要通过MemTableIterator遍历写出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// builder.cc
Status BuildTable(const std::string& dbname,
Env* env,
const Options& options,
TableCache* table_cache,
Iterator* iter,
FileMetaData* meta) {
Status s;
meta->file_size = 0;
iter->SeekToFirst(); // MemTable 迭代器初始化
std::string fname = TableFileName(dbname, meta->number); // 获取sst文件名称:{sst_number}.ldb
if (iter->Valid()) {
WritableFile* file;
s = env->NewWritableFile(fname, &file); // 创建sst文件刷写句柄
if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
TableBuilder* builder = new TableBuilder(options, file); // SST 构造器
meta->smallest.DecodeFrom(iter->key()); // 在 file_meta 中记录最小 key
Slice key;
// 迭代MemTable中的数据并提交给TableBuilder
for (; iter->Valid(); iter->Next()) {
key = iter->key();
builder->Add(key, iter->value());
}
。。。
// 完成构建, 做 datablock, filterblock, metaindexblock, indexblock, footer收尾工作
s = builder->Finish();
。。。
}
。。。
}
BuildTable中,将基于MemTableIterator迭代MemTable并写出数据。 由此可见,每一个MemTable将形成一个SST文件。
数据在提交给TableBuilder::Add时, 每个DataBlock数据大小将限制在r->options.block_size(默认4KB)。
每当DataBlock数据超过限制时, 将触发写DataBlock写操作, 同时将构建此DataBlock中的BloomFilter,并在IndexBlock中添加索引信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
***
* <pre>
* 数据写入 sstable:
* 1. key 的写入顺序为有序, 依次递增。
* 2. 写入 datablock 之前首先写入 filter_block
* 3. 写入datablock
* 4. 如果 datablock 超过限制,进行datablock 刷盘操作
* 5. 如果刷盘操作,在 index_block 中记录上个 datablock 的索引位置
* </pre>
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
void TableBuilder::Add(const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
Rep* r = rep_; // 获得引用
assert(!r->closed);
if (!ok()) return; // 记录写入状态
if (r->num_entries > 0) {
// 要求排序递增
assert(r->options.comparator->Compare(key, Slice(r->last_key)) > 0);
}
if (r->pending_index_entry) {
/**
* 上一个 datablock 写入完成, 需要记录一下 datablock 的index 信息
* index_block 数据存储:
* 格式 : block_builder
* key : 上次写入的key(r->last_key)
* value : pending_handle(上一个datablock 写入前的offset, 上一个datablock size)
*
*/
assert(r->data_block.empty());
// 比较并截断 last_key
r->options.comparator->FindShortestSeparator(&r->last_key, key);
std::string handle_encoding;
r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding); // 序列化出偏移
r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding)); // 记录last key 的偏移位置
r->pending_index_entry = false;
}
if (r->filter_block != nullptr) {
// Bloom 过滤器需要写入 key
r->filter_block->AddKey(key);
}
// 将插入的 key 标志入 last_key
r->last_key.assign(key.data(), key.size());
r->num_entries++; // 数据元素增一
r->data_block.Add(key, value); // datablock 插入元素
const size_t estimated_block_size = r->data_block.CurrentSizeEstimate(); // 计算 datablock 当前数据量的大小
// 如果 datablock 数据量的大小超过设置的 block_size
// 则 进行刷写操作
if (estimated_block_size >= r->options.block_size) {
Flush();
}
}
可以看出如果 DataBlock 超过一定的大小,则刷盘,重新写一个 DataBlock, 这时在 IndexBlock 中记录一下写完成 DataBlock 的索引位置。
等到所有的 Key-Value 都写完以后:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
/***
* 数据写入完成, 进行归档操作 :
* | data_block_1 | data_block_2 | ... | data_block_n |
* | filter_block |
* | meta_index_block |
* | index_block |
* | footer |
* @return
*/
Status TableBuilder::Finish() {
Rep* r = rep_;
// Data Block 剩余数据落盘
Flush();
assert(!r->closed);
r->closed = true;
BlockHandle filter_block_handle, metaindex_block_handle, index_block_handle;
// Filter Block 数据落盘
if (ok() && r->filter_block != nullptr) {
WriteRawBlock(r->filter_block->Finish(), kNoCompression, &filter_block_handle);
}
// Meta index block 数据落盘
// key : 过滤器名称
// value : 过滤器 BlockHandle
if (ok()) {
BlockBuilder meta_index_block(&r->options);
if (r->filter_block != nullptr) {
// 记录过滤器名称
std::string key = "filter.";
key.append(r->options.filter_policy->Name());
// 记录过滤器的位置索引信息
std::string handle_encoding;
filter_block_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
meta_index_block.Add(key, handle_encoding);
}
// TODO(postrelease): Add stats and other meta blocks
WriteBlock(&meta_index_block, &metaindex_block_handle);
}
// IndexBlock 数据落盘
// key : last_key
// value : last_key 对应的 datablock 的 BlockHandle
if (ok()) {
if (r->pending_index_entry) {
r->options.comparator->FindShortSuccessor(&r->last_key);
std::string handle_encoding;
r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding));
r->pending_index_entry = false;
}
WriteBlock(&r->index_block, &index_block_handle);
}
// 写 Footer 数据落盘
// metaindex_block_handle 元信息记录
// index_block_handle 元信息记录
// kTableMagicNumber 数据落地
if (ok()) {
// 填充 Footer 数据
Footer footer;
footer.set_metaindex_handle(metaindex_block_handle);
footer.set_index_handle(index_block_handle);
// 序列化数据
std::string footer_encoding;
footer.EncodeTo(&footer_encoding);
// 写入文件
r->status = r->file->Append(footer_encoding);
if (r->status.ok()) {
r->offset += footer_encoding.size();
}
}
return r->status;
}
由此完成了一个 SST 的数据写入。
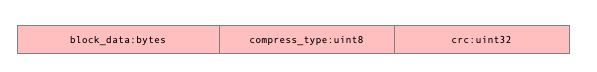
需要说明的是: DataBlock, IndexBlock, MetaIndexBlock. 数据落地可能会经过一层压缩, 其压缩策略收到r->options.compression控制,支持Snappy压缩方式。
它的数据块落地到文件格式为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// table_builder.cc
void TableBuilder::WriteBlock(BlockBuilder* block, BlockHandle* handle) {
assert(ok());
Rep* r = rep_;
// 填充 block 剩余信息
// - block 的每一个重启点
// - block 的重启点个数
Slice raw = block->Finish();
Slice block_contents;
CompressionType type = r->options.compression; // 获取压缩类型
// 是否进行压缩
switch (type) {
case kNoCompression:
block_contents = raw;
break;
case kSnappyCompression: {
std::string* compressed = &r->compressed_output;
if (port::Snappy_Compress(raw.data(), raw.size(), compressed) &&
compressed->size() < raw.size() - (raw.size() / 8u)) {
block_contents = *compressed;
} else {
// Snappy not supported, or compressed less than 12.5%, so just
// store uncompressed form
block_contents = raw;
type = kNoCompression;
}
break;
}
}
// block 数据落盘
WriteRawBlock(block_contents, type, handle);
r->compressed_output.clear();
// 清空 block 缓存
block->Reset();
}