Spark 源码 | Spark On Yarn/k8s
本文通过阅读 Spark deploy 相关部分的代码,了解学习 spark 分布式资源调度的架构实现以及原理和细节。
参考的 spark 版本为 2.3.1.
在spark源码中,主要实现了三种分布式环境下的资源申请与作业调度方案,他们分别是 :
- yarn : https://github.com/Aiden-Dong/spark-2.3.1/tree/master/resource-managers/yarn
- kubernetes : https://github.com/Aiden-Dong/spark-2.3.1/tree/master/resource-managers/kubernetes
- mesos : https://github.com/Aiden-Dong/spark-2.3.1/tree/master/resource-managers/mesos
我们下面主要介绍下 yarn, kubernetes 环境下的资源调度实现。
SchedulerBackend : 资源调度的本质
分布式情况下的资源调度框架是相同的,服务的交互依赖于 RPC 的相关模块, 有关 RPC 可以阅读 : https://aiden-dong.github.io/2019/12/12/spark%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E4%B9%8BRPC%E7%AF%87/ 部分。
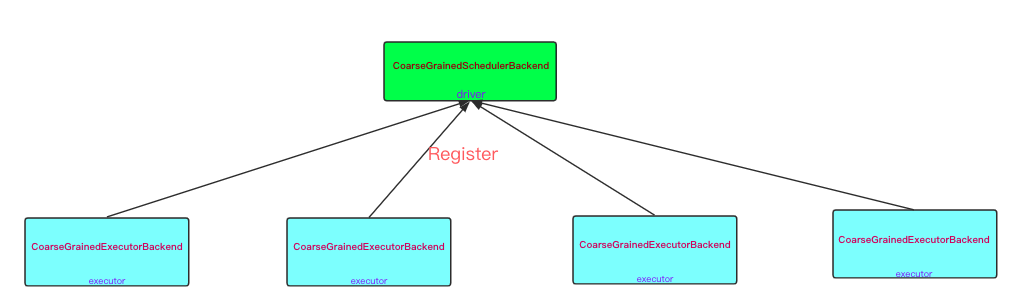
在分布式下面, driver 端的类实现为 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 的相关派生类。 executor 端的类实现为 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.
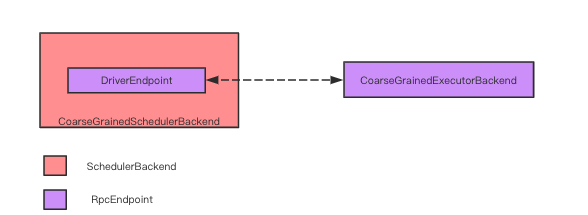
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 是 SchedulerBackend 的派生类, 其主要作用是检查当前是否有可用的资源,并负责将需要调度的作业提交到相应的executor中.
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 内部使用 DriverEndpoint 与 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 通信, DriverEndpoint 与 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 本质上是一个 RpcEndpoint。两者通过 Netty 实现通信。
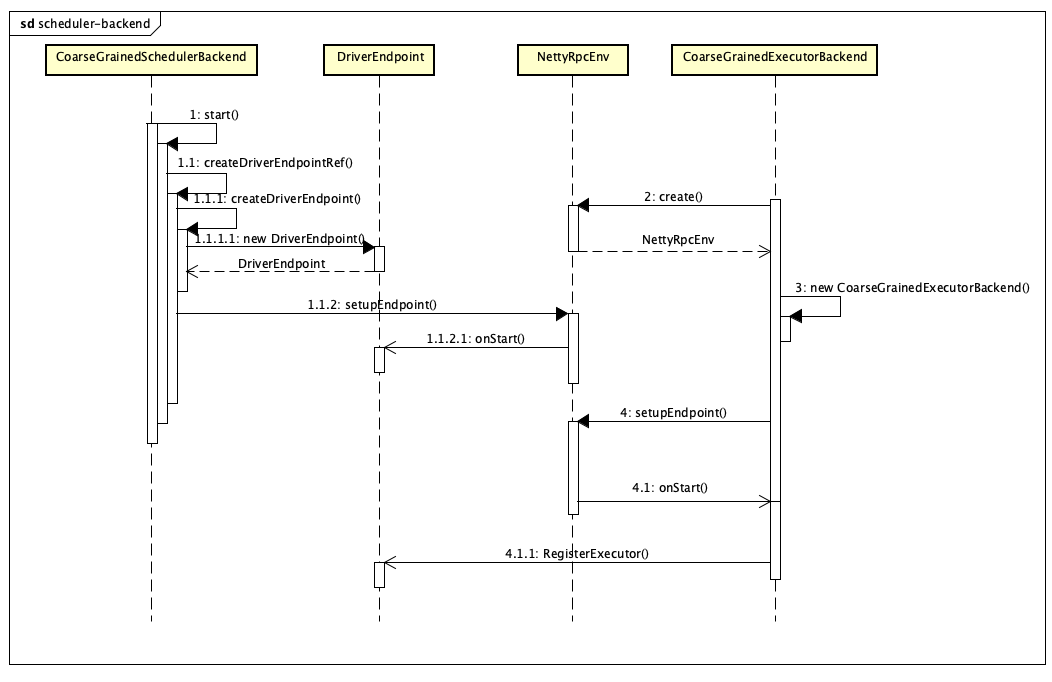
driver 端服务CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend首先被启动, 然后在根据需求executor数量,在启动相应数量的 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend. CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 在启动时根据 driver DriverEndpoint 的地址建立链接。 发起注册申请,将自己注册到 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 中。
driver 端的启动建立逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
val ENDPOINT_NAME = "CoarseGrainedScheduler"
override def start() {
。。。
// TODO (prashant) send conf instead of properties
driverEndpoint = createDriverEndpointRef(properties)
}
protected def createDriverEndpointRef(
properties: ArrayBuffer[(String, String)]): RpcEndpointRef = {
rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(ENDPOINT_NAME, createDriverEndpoint(properties))
}
class DriverEndpoint(override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv, sparkProperties: Seq[(String, String)])
extends ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint with Logging {
protected val executorsPendingLossReason = new HashSet[String]
protected val addressToExecutorId = new HashMap[RpcAddress, String]
override def onStart() {
// 启动时初始化动作
}
/**
* 无响应 RPC 请求
*/
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) =>
// task 状态更新消息
scheduler.statusUpdate(taskId, state, data.value)
。。。
case ReviveOffers =>
makeOffers()
case KillTask(taskId, executorId, interruptThread, reason) =>
// task kill 信息
。。。
case KillExecutorsOnHost(host) =>
// executor kill 信息
case UpdateDelegationTokens(newDelegationTokens) =>
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
// executor remove 信息
}
/**
* 响应式 RPC 请求信息
*/
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
// Executor 注册消息
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
// RegisterExecutorFailed
} else if (scheduler.nodeBlacklist != null &&scheduler.nodeBlacklist.contains(hostname)) {
// RegisterExecutorFailed
} else {
...
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorAddress, hostname,cores, cores, logUrls)
...
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
...
makeOffers()
}
case StopDriver =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case StopExecutors =>
...
for ((_, executorData) <- executorDataMap) {
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor)
}
...
case RemoveWorker(workerId, host, message) =>
...
removeWorker(workerId, host, message)
...
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig =>
...
}
// 更新资源提交作业
private def makeOffers() {
// Make sure no executor is killed while some task is launching on it
// 提交给 TaskScheduler 来分配任务
val taskDescs = CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
// Filter out executors under killing
// 过滤掉正在被杀死的executor
val activeExecutors = executorDataMap.filterKeys(executorIsAlive)
// 把所有可用的executor封装成资源对象
val workOffers = activeExecutors.map {
case (id, executorData) =>
new WorkerOffer(id, executorData.executorHost, executorData.freeCores)
}.toIndexedSeq
// 把这些可用的资源交给TaskSchedulerImpl进行调度
// TaskSchedulerImpl 会综合考虑任务本地性,黑名单,调度池的调度顺序等因素,返回TaskDescription集合
// TaskDescription对象是对一个Task的完整描述,
// 包括序列化的任务数据,任务在哪个executor上运行,依赖文件和jar包等信息
scheduler.resourceOffers(workOffers)
}
if (!taskDescs.isEmpty) {
// 首先还得接着回到 DriverEndpoint.makeOffers 方法,makeOffers方法中通过调用 TaskSchedulerImpl.resourceOffers 方法切入 TaskSchedulerImpl ,
// 然后就是 TaskSchedulerImpl 在做任务分配的工作,最终 TaskSchedulerImpl 将分配好的任务以TaskDescription的封装形式返回给DriverEndpoint(DriverEndpoint是调度后端的一个内部类).
// 然后紧接着调用 DriverEndpoint.launchTasks 方法将这些任务传给相应的executor执行。
launchTasks(taskDescs)
}
}
private def launchTasks(tasks: Seq[Seq[TaskDescription]]) {
for (task <- tasks.flatten) {
val serializedTask = TaskDescription.encode(task)
...
// 维护cpu资源信息
val executorData = executorDataMap(task.executorId)
executorData.freeCores -= scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASK
// 通过rpc发送任务到指定的executor上
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))
}
}
private def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
。。。
}
private def removeWorker(workerId: String, host: String, message: String): Unit = {
。。。
}
protected def disableExecutor(executorId: String): Boolean = {
。。。
}
}
executor 端的启动建立逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
def main(args: Array[String]) {
。。。
run(driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, appId, workerUrl, userClassPath)
System.exit(0)
}
private def run(
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
appId: String,
workerUrl: Option[String],
userClassPath: Seq[URL]) {
。。。
// 建立 Netty RPC
val fetcher = RpcEnv.create("driverPropsFetcher",hostname, -1, executorConf, new SecurityManager(executorConf), clientMode = true)
// 建立与 driver 的链接
val driver = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl)
// 获取配置
val cfg = driver.askSync[SparkAppConfig](RetrieveSparkAppConfig)
val props = cfg.sparkProperties ++ Seq[(String, String)](("spark.app.id", appId))
fetcher.shutdown()
// Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver.
val driverConf = new SparkConf()
for ((key, value) <- props) {
// this is required for SSL in standalone mode
if (SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf(key)) {
driverConf.setIfMissing(key, value)
} else {
driverConf.set(key, value)
}
}
。。。
val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(driverConf, executorId, hostname, cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", new CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(env.rpcEnv, driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, userClassPath, env))
。。。
}
}
private[spark] class CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
userClassPath: Seq[URL],
env: SparkEnv)
extends ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint with ExecutorBackend with Logging {
private[this] val stopping = new AtomicBoolean(false)
var executor: Executor = null
@volatile var driver: Option[RpcEndpointRef] = None
private[this] val ser: SerializerInstance = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
override def onStart() {
// 初始化
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// 注册到 driver
driver = Some(ref)
ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
...
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisteredExecutor =>
// 注册成功
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
case RegisterExecutorFailed(message) =>
// 注册失败
case LaunchTask(data) =>
// 运行作业
executor.launchTask(this, taskDesc)
case KillTask(taskId, _, interruptThread, reason) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received KillTask command but executor was null")
} else {
executor.killTask(taskId, interruptThread, reason)
}
case StopExecutor =>
。。。
case Shutdown =>
。。。
case UpdateDelegationTokens(tokenBytes) =>
。。。
}
}
所以每当executor 启动后, 会根据 driver 的信息自动向 driver 的DriverEndpoint发起注册请求。这时候每个 executor 的相关信息被维护到 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 的executorDataMap 变量中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
private val executorDataMap = new HashMap[String, ExecutorData]
private[cluster] class ExecutorData(
val executorEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef,
val executorAddress: RpcAddress,
override val executorHost: String,
var freeCores: Int,
override val totalCores: Int,
override val logUrlMap: Map[String, String]
) extends ExecutorInfo(executorHost, totalCores, logUrlMap)
当driver端接受到来自TaskScheduler或者其他地方的资源更新需求时, 检查自己的executor剩余情况并将资源交给TaskScheduler去调度作业. 完成后,将调度作业信息通过makeOffers发送给指定的executor去执行。 (TaskScheduler 过程可以参见 https://aiden-dong.github.io/2019/12/09/spark%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E4%B9%8B%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E7%AF%87/)
Spark On Yarn
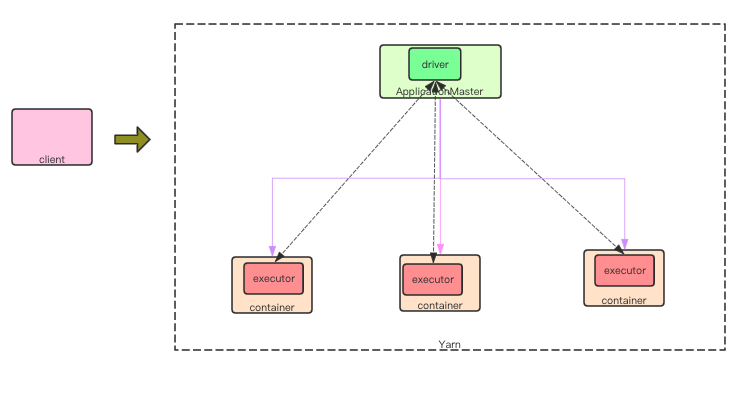
spark on yarn 环境下允许用户指定 --deploy-mode 为 cluster or client. 即将 driver 端放在本地执行或者在 Yarn Application Master 上。 其他地方都大致相同。
cluster mode
cluster 模式 driver 在ApplicationMaster中执行。 程序首先加载org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication作为启动类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
private[deploy] val YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication"
private def doPrepareSubmitEnvironment(
args: SparkSubmitArguments,
conf: Option[HadoopConfiguration] = None)
: (Seq[String], Seq[String], SparkConf, String) = {
...
val isYarnCluster = clusterManager == YARN && deployMode == CLUSTER
...
if (isYarnCluster) {
childMainClass = YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS
...
}
...
}
private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication {
override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = {
// SparkSubmit would use yarn cache to distribute files & jars in yarn mode,
// so remove them from sparkConf here for yarn mode.
conf.remove("spark.jars")
conf.remove("spark.files")
new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf).run()
}
}
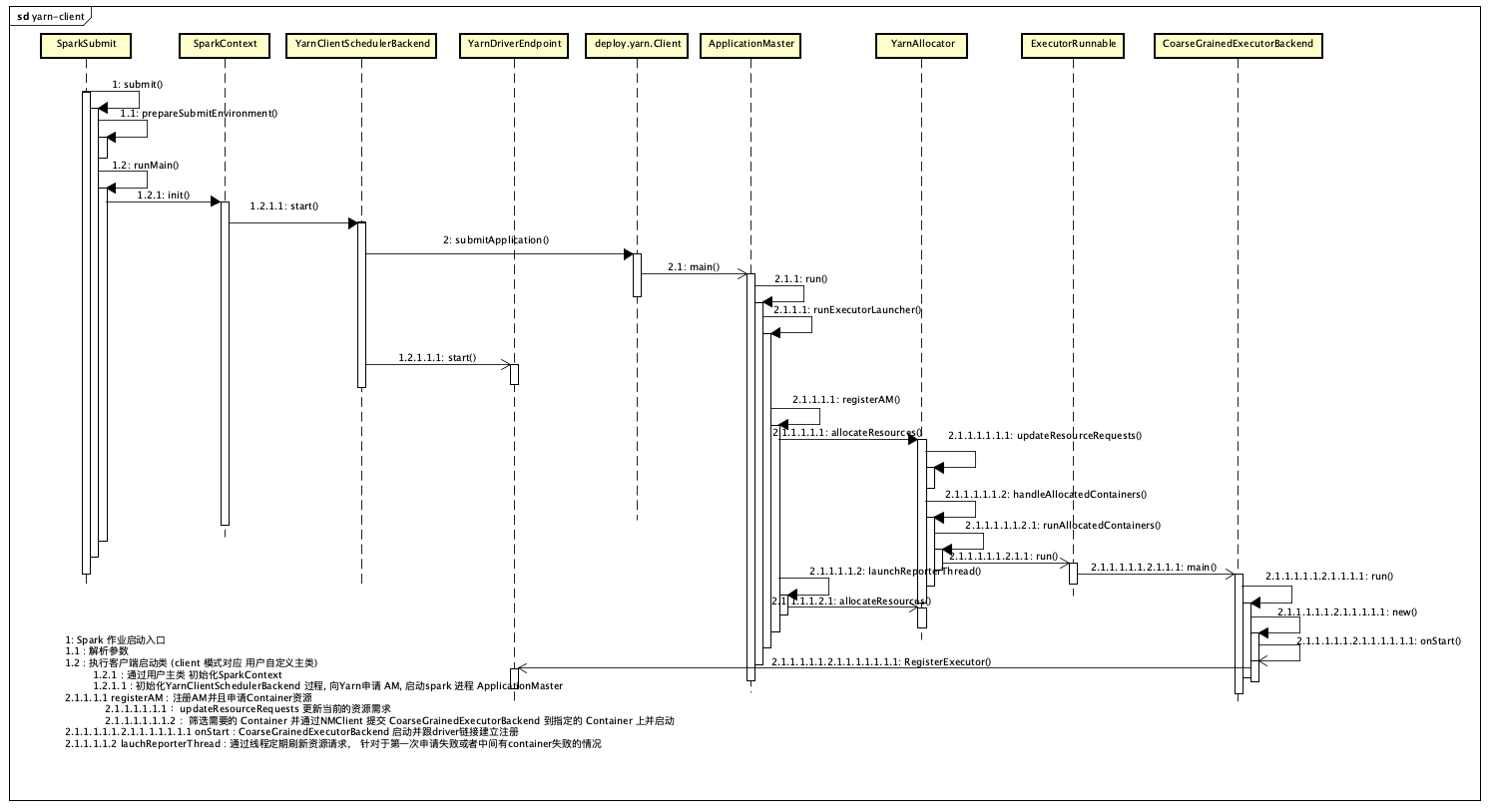
Yarn 资源的申请 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client.submitApplication() 完成。
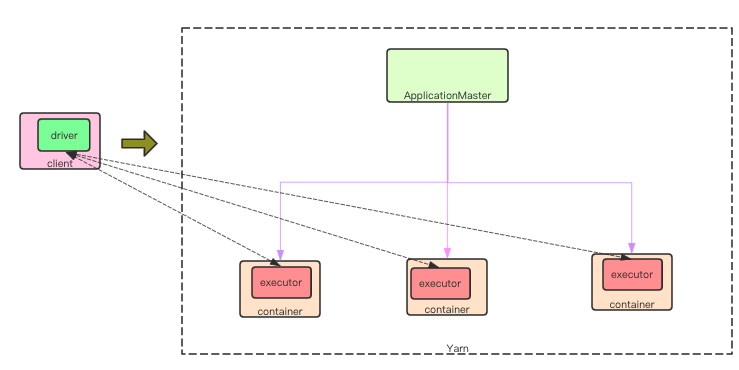
client mode
client 模式 driver 在client中执行。 程序首先加载用户启用主类作为启动类。
在 SparkContext 初始化过程中, 使用 YarnClusterManager 创建YarnClientSchedulerBackend, 作为其SchedulerBackend. 在其初始化过程中同样调用 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client.submitApplication() 初始化 yarn 资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
override def start() {
。。。
client = new Client(args, conf)
bindToYarn(client.submitApplication(), None)
。。。
}
Yarn ApplicationMaster 初始化
org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client.submitApplication() 过程使用 YarnClient 去RM申请资源去建立 ApplicationMaster。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {
var appId: ApplicationId = null
...
yarnClient.init(hadoopConf)
yarnClient.start()
val newApp = yarnClient.createApplication() // 创建一个Application
val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse() // 获取资源情况
appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId()
verifyClusterResources(newAppResponse) // 校验内存请求是否合理
val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse) // 设置执行的环境与执行的命令
val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext) // 设置资源需求
yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext) // 提交作业
。。。
appId
}
private def createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse: GetNewApplicationResponse)
: ContainerLaunchContext = {
。。。
val launchEnv = setupLaunchEnv(appStagingDirPath, pySparkArchives) // 环境
val localResources = prepareLocalResources(appStagingDirPath, pySparkArchives) // 依赖
val amContainer = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext])
amContainer.setLocalResources(localResources.asJava)
amContainer.setEnvironment(launchEnv.asJava)
// 命令
val javaOpts = ListBuffer[String]()
。。。
val userClass =
if (isClusterMode) {
Seq("--class", YarnSparkHadoopUtil.escapeForShell(args.userClass))
} else {
Nil
}
val amClass =
if (isClusterMode) {
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster").getName // cluster
} else {
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher").getName // client
}
val amArgs =
Seq(amClass) ++ userClass ++ userJar ++ primaryPyFile ++ primaryRFile ++ userArgs ++
Seq("--properties-file", buildPath(Environment.PWD.$$(), LOCALIZED_CONF_DIR, SPARK_CONF_FILE))
val commands = prefixEnv ++
Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++
javaOpts ++ amArgs ++
Seq(
"1>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stdout",
"2>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stderr")
// TODO: it would be nicer to just make sure there are no null commands here
val printableCommands = commands.map(s => if (s == null) "null" else s).toList
amContainer.setCommands(printableCommands.asJava)
。。。
amContainer
}
当 client 向RM申请一个 AppMaster 后, 如果是 cluster 模式,将启用 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster。 而如果是 client 模式, 将启用 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher。
不过虽然调用类不一样, 但是最终都会转到 ApplicationMaster.
1
2
3
4
5
object ExecutorLauncher {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
ApplicationMaster.main(args)
}
}
在 ApplicationMaster 里面会检查提交模式为clientorcluster, 根据提交模式的不同, 选择是否在 Yarn AM 上启动 driver.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
private def runImpl(): Unit = {
。。。
if (isClusterMode) {
runDriver()
} else {
runExecutorLauncher()
}
。。。
}
最终, ApplicationMaster 根据需要的资源数量, 申请指定数量的 Container 加载 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 主类, 启动executor 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
private def runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse: ArrayBuffer[Container]): Unit = {
for (container <- containersToUse) {
...
if (runningExecutors.size() < targetNumExecutors) {
numExecutorsStarting.incrementAndGet()
if (launchContainers) {
launcherPool.execute(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
...
new ExecutorRunnable(
Some(container),
conf,
sparkConf,
driverUrl,
executorId,
executorHostname,
executorMemory,
executorCores,
appAttemptId.getApplicationId.toString,
securityMgr,
localResources
).run()
updateInternalState()
...
}
})
} else {
// For test only
updateInternalState()
}
} else {
logInfo(("Skip launching executorRunnable as running executors count: %d " +
"reached target executors count: %d.").format(
runningExecutors.size, targetNumExecutors))
}
}
}
Yarn Container 初始化
ApplicationMaster 端向 Container 启动服务过程如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
nmClient = NMClient.createNMClient()
nmClient.init(conf)
nmClient.start()
val ctx = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext])
.asInstanceOf[ContainerLaunchContext]
val env = prepareEnvironment().asJava
ctx.setLocalResources(localResources.asJava)
ctx.setEnvironment(env)
val credentials = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getCredentials()
val dob = new DataOutputBuffer()
credentials.writeTokenStorageToStream(dob)
ctx.setTokens(ByteBuffer.wrap(dob.getData()))
val commands = prepareCommand()
ctx.setCommands(commands.asJava)
ctx.setApplicationACLs(
YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getApplicationAclsForYarn(securityMgr).asJava)
nmClient.startContainer(container.get, ctx)
提交到 Container 中执行的命令为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
val commands = prefixEnv ++
Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++
javaOpts ++
Seq("org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend",
"--driver-url", masterAddress,
"--executor-id", executorId,
"--hostname", hostname,
"--cores", executorCores.toString,
"--app-id", appId) ++
userClassPath ++
Seq(s"1>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stdout",
s"2>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stderr")
这样就把 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 提交到指定的Container中并启动了。
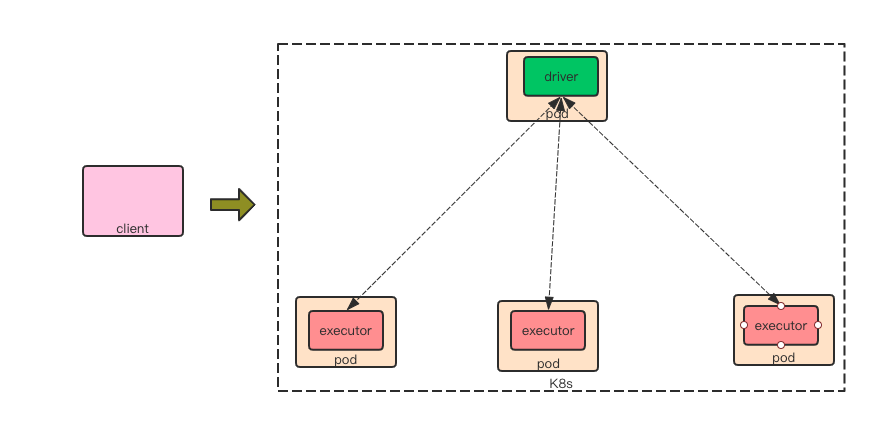
Spark on k8s
在 spark on k8s 过程跟 spark on yarn 的 cluster 模式大致相同, 在 2.3 里面暂时还不支持 client 模式。
首先客户端先向服务端申请 pod 去执行用户主类:
pod 大致如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: {spark.kubernetes.driver.pod.name}
namespace: {spark.kubernetes.namespace}
labels:
...
volumes :
- name : download-jars-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name : download-files-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name : spark-init-properties
emptyDir: {}
spec:
restartPolicy : Never
nodeSelector : {spark.kubernetes.node.selector.*}
containers:
- name: spark-kubernetes-driver
image:
{spark.kubernetes.container.image}
imagePullPolicy : {spark.kubernetes.container.image.pullPolicy}
env:
- name : SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY
value : {spark.driver.memory}
- name : SPARK_DRIVER_CLASS
value : {userMinClass}
- name : SPARK_DRIVER_ARGS
value : {userArgs}
- name : SPARK_DRIVER_BIND_ADDRESS
value : {-> v1 status.podIP}
volumeMounts:
- name : download-jars-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-jars
- name : download-files-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-files
resources:
limits:
cpu : {spark.kubernetes.driver.limit.cores}
memory : {spark.driver.memoryOverhead} + {spark.driver.memory}
requests :
cpu : {spark.driver.cores}
memory : {spark.driver.memory}
args : driver
initContainers:
- name : spark-init
image:
{spark.kubernetes.container.image}
imagePullPolicy : {spark.kubernetes.container.image.pullPolicy}
volumeMounts:
- name : download-jars-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-jars
- name : download-files-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-files
- name : spark-init-properties
value : /etc/spark-init
args :
- init
- /etc/spark-init/spark-init.properties
initContainers 不是所有的spark任务都有的, 它主要用于远程文件的下载, 如果有文件不在本地, 将在创建时增加initContainers 与我们任务的container 挂载同一个盘, 并执行下载任务。 下面的 executor 也是如此
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: {spark.kubernetes.executor.podNamePrefix}-exec-{executorId}
namespace: {spark.kubernetes.namespace}
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion : {driverPod.getApiVersion}
controller : true
kind: {driverPod.getKind}
name: {driverPod.getMetadata.getName}
uid: {driverPod.getMetadata.getUid}
labels:
...
volumes :
- name : download-jars-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name : download-files-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name : spark-init-properties
emptyDir: {}
spec:
restartPolicy : Never
nodeSelector : {spark.kubernetes.node.selector.*}
containers:
- name: executor
image:
{spark.kubernetes.container.image}
imagePullPolicy : {spark.kubernetes.container.image.pullPolicy}
env:
- name : {SPARK_DRIVER_URL}
value : {driverUrl}
- name : {SPARK_EXECUTOR_CORES}
value : {spark.executor.cores}
- name : SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY
value : {spark.executor.memory}
- name : SPARK_EXECUTOR_ID
value : {executorId}
- name : SPARK_EXECUTOR_POD_IP
value : {v1 -> status.podIP}
- name : SPARK_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH
value : /var/spark-data/spark-jars/*
volumeMounts:
- name : download-jars-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-jars
- name : download-files-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-files
resources:
limits:
cpu : {spark.kubernetes.executor.limit.cores}
memory : {spark.executor.memoryOverhead} + {spark.executor.memory}
requests :
cpu : {spark.executor.cores}
memory : {spark.executor.memory}
ports :
- containerPort: {spark.blockmanager.port}
args : executor
initContainers:
- name : spark-init
image:
{spark.kubernetes.container.image}
imagePullPolicy : {spark.kubernetes.container.image.pullPolicy}
volumeMounts:
- name : download-jars-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-jars
- name : download-files-volume
value : /var/spark-data/spark-files
- name : spark-init-properties
value : /etc/spark-init
args :
- init
- /etc/spark-init/spark-init.properties
我们看下镜像编排文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
FROM openjdk:8-alpine
ARG spark_jars=jars
ARG img_path=kubernetes/dockerfiles
RUN set -ex && \
apk upgrade --no-cache && \
apk add --no-cache bash tini libc6-compat && \
mkdir -p /opt/spark && \
mkdir -p /opt/spark/work-dir \
touch /opt/spark/RELEASE && \
rm /bin/sh && \
ln -sv /bin/bash /bin/sh && \
chgrp root /etc/passwd && chmod ug+rw /etc/passwd
COPY ${spark_jars} /opt/spark/jars
COPY bin /opt/spark/bin
COPY sbin /opt/spark/sbin
COPY conf /opt/spark/conf
COPY ${img_path}/spark/entrypoint.sh /opt/
COPY examples /opt/spark/examples
COPY data /opt/spark/data
ENV SPARK_HOME /opt/spark
WORKDIR /opt/spark/work-dir
ENTRYPOINT [ "/opt/entrypoint.sh" ]
通过 /opt/entrypoint.sh 来引导启动我们的服务。 在 entrypoint.sh 里面根据参数的不同执行不同的应用。
driver 通过用户主类加载 SparkContext, 通过内部初始化的 KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend 主类来申请其他的 pod, 同样通过 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 启动 executor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
case "$SPARK_K8S_CMD" in
driver)
CMD=(
${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java
"${SPARK_JAVA_OPTS[@]}"
-cp "$SPARK_CLASSPATH"
-Xms$SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY
-Xmx$SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY
-Dspark.driver.bindAddress=$SPARK_DRIVER_BIND_ADDRESS
$SPARK_DRIVER_CLASS
$SPARK_DRIVER_ARGS
)
;;
executor)
CMD=(
${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java
"${SPARK_JAVA_OPTS[@]}"
-Xms$SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY
-Xmx$SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY
-cp "$SPARK_CLASSPATH"
org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
--driver-url $SPARK_DRIVER_URL
--executor-id $SPARK_EXECUTOR_ID
--cores $SPARK_EXECUTOR_CORES
--app-id $SPARK_APPLICATION_ID
--hostname $SPARK_EXECUTOR_POD_IP
)
;;
init)
CMD=(
"$SPARK_HOME/bin/spark-class"
"org.apache.spark.deploy.k8s.SparkPodInitContainer"
"$@"
)
;;
参考内容