Leveldb 教程 | Leveldb 数据读取流程
leveldb 数据读取经过三个阶段 :
- 从MemTable中查找数据
- 从IMemTable(将要被刷到磁盘的MemTable)中查找数据
- 从SST中查找数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// db_impl.cc
// DBImpl::Get 方法
{
mutex_.Unlock();
LookupKey lkey(key, snapshot);
if (mem->Get(lkey, value, &s)) { // 从MemTable中读取数据
// Done
} else if (imm != nullptr && imm->Get(lkey, value, &s)) { // 从IMemTable中读取数据
// Done
} else {
s = current->Get(options, lkey, value, &stats); // 从SST中读取数据
have_stat_update = true;
}
mutex_.Lock();
}
用户查询的UserKey会被封装成LookupKey结构进行查询,它本质就是一个InternalKey
他通过序列号支持查询历史版本,默认查询最新版本(sequencenumber取最大)。
本质来说MemTable与IMemTable都是一个基于内存的MemTable结构,其数据结构我们之前说过不在描述,有需要请移步MemTable 数据结构。
MemTable数据查询:
它将LookupKey转换成与MemTable中维护的entry相近的一种表示: |internal_key_len | user_key | sequence_number |
它在内部基于SkipList查找大于等于用户提交的internal_key的数据(基于InternalKeyComparator的比较策略)。
找到数据以后,因为拿到的是大于等于的结果,所以进行user_key与ValueType的精确比对查询。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
bool MemTable::Get(const LookupKey& key, std::string* value, Status* s) {
Slice memkey = key.memtable_key(); // 返回key的 MemTable 表示法 | key_lenth | user_key | seqnumber |
Table::Iterator iter(&table_);
// 本质是调用 FindGreaterOrEqual 查找大于等于(使用InternalKeyComparator)InternalKey的数据。
iter.Seek(memkey.data());
// 数据已经找到
if (iter.Valid()) {
const char* entry = iter.key(); // 取出数据节点
uint32_t key_length;
const char* key_ptr = GetVarint32Ptr(entry, entry + 5, &key_length);
// 因为拿到的是大于等于目标key的数据, 所以需要取出user_key进行精确比对
if (comparator_.comparator.user_comparator()->Compare(Slice(key_ptr, key_length - 8), key.user_key()) == 0) {
const uint64_t tag = DecodeFixed64(key_ptr + key_length - 8); // 获取序列号
// 获取数据类型
switch (static_cast<ValueType>(tag & 0xff)) {
case kTypeValue: { // 如果最新的数据是插入类型,说明数据有效,返回结果
// 获取 value
Slice v = GetLengthPrefixedSlice(key_ptr + key_length);
value->assign(v.data(), v.size());
return true;
}
case kTypeDeletion: // 如果最新的数据是删除类型,说明数据无效已经被删除
*s = Status::NotFound(Slice());
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
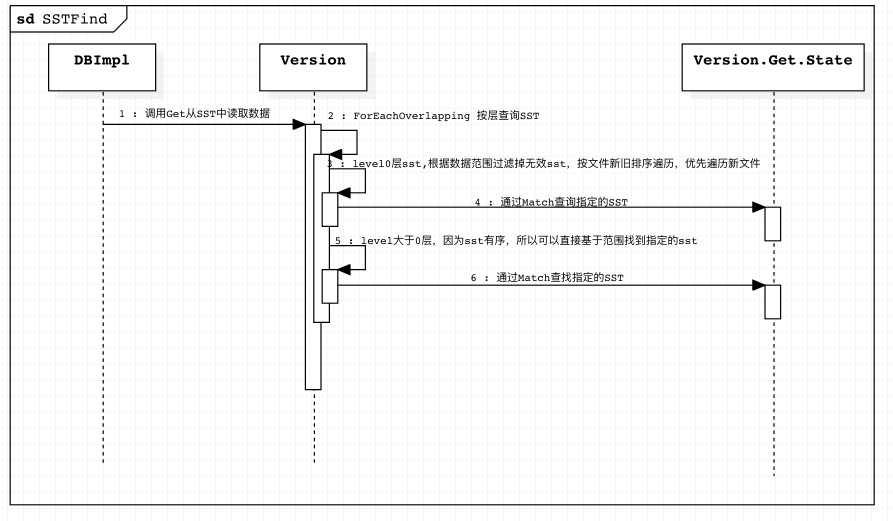
SST 数据整体查询逻辑
如果数据没有在MemTable中也不在IMemTable中,此时数据需要在SST中查询。
因为在CURRENT VERSION中维护这所有的有效SST, 并且记录其level信息。 所以提交请求会经过Version取查询。
因为level0层数据与其他level层SST排列方式并不相同:
- 因为level0层SST是从MemTable中dump下来的,所以SST之间数据可能存在重叠,但是它也有新旧之分,sst文件编码越大,代表sst被刷盘的时间越新。
- 其他level层同层的sst之间数据是不会重叠的切有序排列,形如 :
[0-49], [50-70], [71-100] - 对于指定的
key进行查询时,需要从最低的level往上查询, 因为对于指定的key来说,他所在sst的level越大,表示数据越旧。
key在level0层的查询方式
当查询level0层数据时, 因为数据会存在重叠,所以要遍历所有的SST, 基于SST的key的范围([smallest, largest]) 判断查询的数据可能会在哪一个sst中。
对于可能存在目标数据的sst, leveldb将他们汇总起来,按照文件编码(sst新旧关系)进行排序,文件编码越大越往前。
然后依次遍历每一个sst,查询数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// version_set.cc
// level == 0, 需要判断所有的文件
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < files_[0].size(); i++) {
FileMetaData* f = files_[0][i]; // level-0 的 filemeta
// 如果文件的 f->smallest < user_key < f->largest
if (ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->smallest.user_key()) >= 0 &&
ucmp->Compare(user_key, f->largest.user_key()) <= 0) {
tmp.push_back(f);
}
}
if (!tmp.empty()) {
// 为了提高顺序, 按照文件的新旧排序
std::sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), NewestFirst);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < tmp.size(); i++) {
// 标识如果无需继续查找,则返回
if (!(*func)(arg, 0, tmp[i])) {
return;
}
}
}
key 在level>=1层数据的查询
当key在level0层没有查询到时,需要在更高的level取查询这个数据。
由于在这些level中,每一层的SST数据不会重叠,且key整体有序。
这样每一层可以采用二分查找, 来快速定位可能存在目标数据的SST.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
int FindFile(const InternalKeyComparator& icmp,
const std::vector<FileMetaData*>& files,
const Slice& key) {
uint32_t left = 0;
uint32_t right = files.size();
while (left < right) {
uint32_t mid = (left + right) / 2;
const FileMetaData* f = files[mid];
if (icmp.InternalKeyComparator::Compare(f->largest.Encode(), key) < 0) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return right;
}
然后在对应的SST中查找数据,直到找到对应的目标数据。
数据在SST内的查询过程
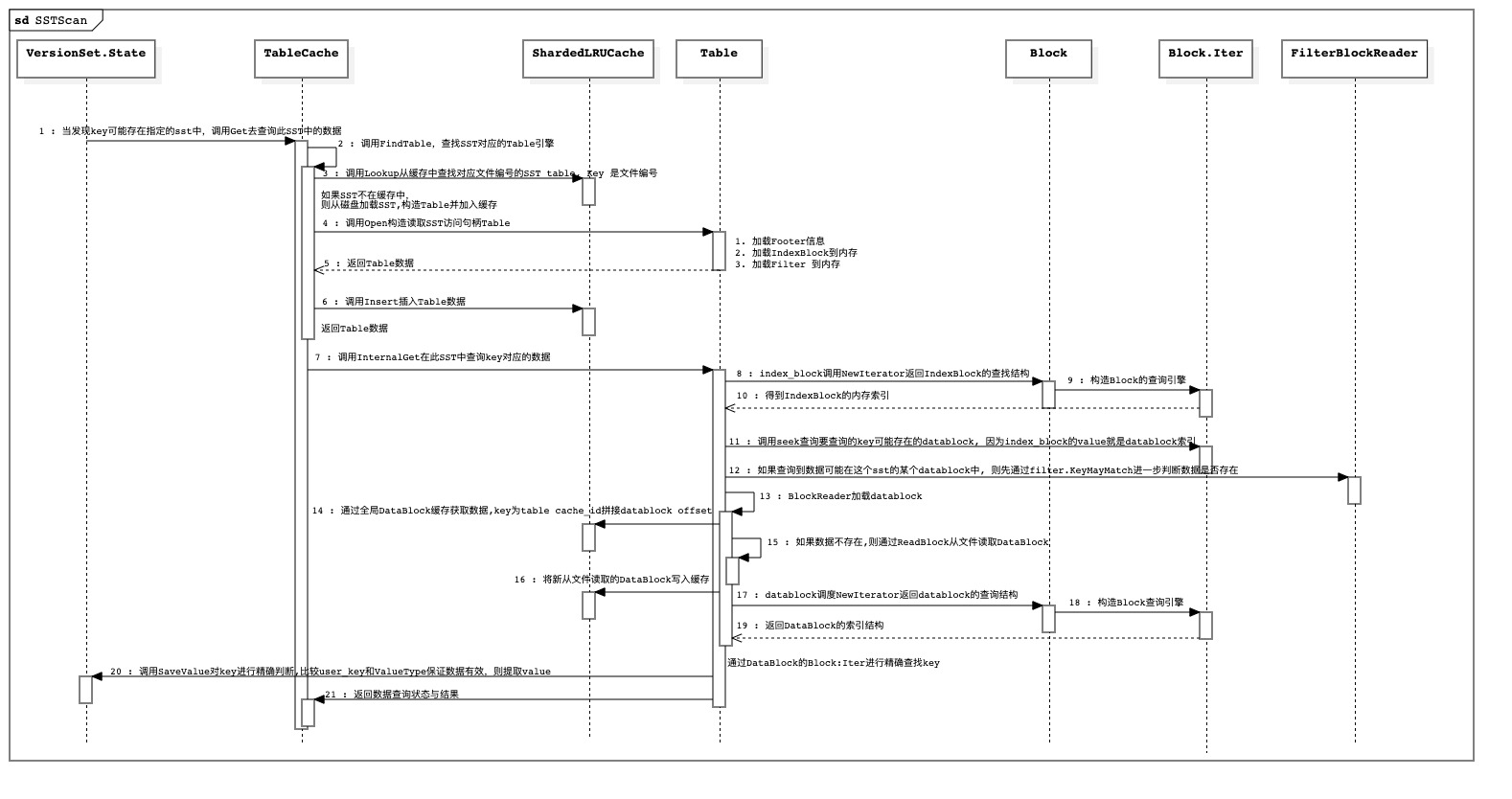
如果数据通过SST的数据范围(FileMetaData[smallest, largest]),怀疑数据在此SST内,需要进入SST查询。 则在SST中需要经过大致如下步骤:
- 读取SST的
Footer,确定MetaIndexBlock与IndexBlock的索引位置 - 读取
MetaIndexBlock,确定FilterBlock的索引位置 - 读取
IndexBlock,基于IndexBlock的key判断数据可能存在的DataBlock - 在读取
DataBlock之前需要拿取FilterBlock判断key是否在对应的DataBlock中 - 如果通过
FilterBlock判断数据确实在对应的DataBlock中, 则读取DataBlock进行精确查询数据
如果请求每次读磁盘会造成磁盘压力过大,所以leveldb中在读取过程增加了缓存,不用每次都去磁盘拉取。
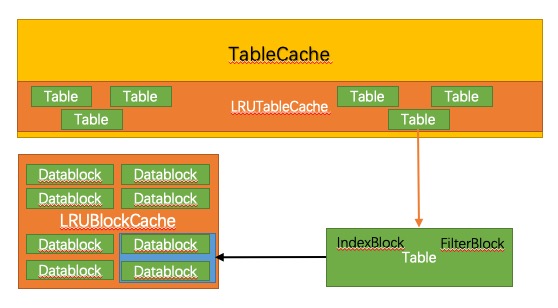
leveldb首先定位到sst的文件信息,基于sst的文件编号判断sst是否位于缓存中,如果为与缓存,则直接从缓存中拿取sst, 否则读取sst文件构建sst的访问结构Table,用于查询sst.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
//table_cache.cc
Status TableCache::Get(const ReadOptions& options, uint64_t file_number, uint64_t file_size, const Slice& k, void* arg,
void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&, const Slice&)) {
Cache::Handle* handle = nullptr;
// 查找SST
Status s = FindTable(file_number, file_size, &handle);
if (s.ok()) {
// 获取SST的操作句柄Table
Table* t = reinterpret_cast<TableAndFile*>(cache_->Value(handle))->table;
// 从Table中查询对应的key
s = t->InternalGet(options, k, arg, handle_result); //从Table中读取
cache_->Release(handle); // 拿到以后要及时释放, 防止内存溢出
}
return s;
}
Status TableCache::FindTable(uint64_t file_number, uint64_t file_size, Cache::Handle** handle) {
Status s;
char buf[sizeof(file_number)];
EncodeFixed64(buf, file_number);
Slice key(buf, sizeof(buf));
*handle = cache_->Lookup(key); // 从 cache 中找到这个文件的缓存,key为文件编号file_number
if (*handle == nullptr) {
// 表示这个 key 不存在缓存中
// 这时候需要从磁盘中读取这个SST
std::string fname = TableFileName(dbname_, file_number); // {dbname_}/{file_number}.ldb
RandomAccessFile* file = nullptr;
Table* table = nullptr;
// 创建sst的随机访问句柄
s = env_->NewRandomAccessFile(fname, &file);
if (!s.ok()) {
std::string old_fname = SSTTableFileName(dbname_, file_number);
if (env_->NewRandomAccessFile(old_fname, &file).ok()) {
s = Status::OK();
}
}
//从sst中读取IndexBlock与FilterBlock,构建Table结构
if (s.ok()) {
s = Table::Open(options_, file, file_size, &table);
}
if (!s.ok()) {
assert(table == nullptr);
delete file;
} else {
TableAndFile* tf = new TableAndFile;
tf->file = file;
tf->table = table;
// 将Table与文件访问句柄放入缓存中,方便下次使用
*handle = cache_->Insert(key, tf, 1, &DeleteEntry);
}
}
return s;
}
Table类是leveldb访问sst的句柄类。它将IndexBlock与FilterBlock直接读取在内存中,他能基于查询key, 大致判断出数据可能存在的DataBlock位置,以及通过BloomFilter判断对应的DataBlock是否存在要查询的key. 这样如果数据不在DataBlock中,能够减少DataBlock的数据扫描。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
//table.cc
Status Table::InternalGet(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& k, void* arg, void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&,const Slice&)) {
Status s;
// 从IndexBlock中定位可能存在key的DataBlock位置
Iterator* iiter = rep_->index_block->NewIterator(rep_->options.comparator);
iiter->Seek(k);
if (iiter->Valid()) {
Slice handle_value = iiter->value(); // 定位到 datablock 的位置
FilterBlockReader* filter = rep_->filter; // 获得过滤器
BlockHandle handle;
// 使用 Bloom 过滤器判断一下数据是否在这个 DataBlock 里面
if (filter != nullptr && handle.DecodeFrom(&handle_value).ok() && !filter->KeyMayMatch(handle.offset(), k)) {
// Bloom 过滤器没有找到这个数据
} else {
// BloomFilter 也判断数据位于这个DataBlock中,那么数据存在的可能性非常大
// 现在进行读取DataBlock查找
// 在DataBlock中进行查找
Iterator* block_iter = BlockReader(this, options, iiter->value());
block_iter->Seek(k);
if (block_iter->Valid()) {
// 找到这个数据,调用回调函数
(*handle_result)(arg, block_iter->key(), block_iter->value());
}
...
}
}
...
}
数据判断数据位于DataBlock中,要进行读取DataBlock数据,这里也是有一个全局的DataBlock缓存。可以减少DataBlock数据IO操作。
LRUCache
leveldb中有两个地方存在LRUCache。一个是TableCache中使用LRUCache缓存已经访问过的SST的Table,其容量为:Options.max_open_files(默认为1000) - 10,每一个Table只会占用一个空间。
另一个是在Options.block_cache中缓存有最近访问的DataBlock,其容量大小为8M。
LRUCache内部有三个数据结构 :
- 用于维护当前处于使用状态的所有缓存元素的双向链表
in_use_ - 用于维护当前缓存在cache但是没有被使用的所有元素的双向链表
lru_ - 用于快速索引缓存数据的
table_
一个数据进入到缓存会被会维护成: LRUHandle 结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
/****
* LRU 缓存节点
* 即用于 hashtable , 又用于lru缓存节点
*/
struct LRUHandle {
void* value; // 具体的值, 指针类型
void (*deleter)(const Slice&, void* value); // 定义回收节点的回调函数
LRUHandle* next_hash; // 使用在hashtable中,挂载同一个hash值上的单链表结构
LRUHandle* next; // 代表 LRU 双向链表中的下一个节点
LRUHandle* prev; // 代表 LRU 双向链表中的上一个节点
size_t charge; // 记录当前 value 所占用的内存大小, 用于后面超出容量后需要进行lru
size_t key_length; // 数据 key 的长度
bool in_cache; // 表示是否在缓存中
uint32_t refs; // 引用计数,因为当前节点可能会被多个组件使用, 不能简单的删除
uint32_t hash; // 记录当前key 的hasn值
char key_data[1]; // key 数据位置
// 获取 key
Slice key() const {
assert(next != this);
return Slice(key_data, key_length);
}
};
如果一个数据元素在缓存中,他要么会被维护在in_use_中,要么会在lru_中。这两个双向链表构成了Cache元素的全集。
为了便于查询,提供了table_结构用来快速查询数据是否在缓存中。它是一个Hash索引结构,内部维护一个数组+链表的结构。 数组用来做hash分桶list_[hash & (length_ - 1)],落在同一个桶里的元素使用链表维护LRUHandle.next_hash。
数组的初始长度为4,按照2的指数倍增长。每当元素数量超过数组长度时就会发生数组扩容事件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
/***
* 在 hash 表中查找元素
* @param key 用于在同一个hash链上的key比对
* @param hash 定位hash点
* @return 指向对应 key 元素的 LRUHandler 指针, 使用二维指针的原因,可能要进行修改操作
*/
LRUHandle** FindPointer(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash) {
LRUHandle** ptr = &list_[hash & (length_ - 1)];
while (*ptr != nullptr && ((*ptr)->hash != hash || key != (*ptr)->key())) {
ptr = &(*ptr)->next_hash;
}
return ptr;
}
LRUHandle* Insert(LRUHandle* h) {
LRUHandle** ptr = FindPointer(h->key(), h->hash); // 查找 hashtable 中是否存在这个节点
LRUHandle* old = *ptr;
h->next_hash = (old == nullptr ? nullptr : old->next_hash);
*ptr = h; // 如果不存在, 进行尾部插入
if (old == nullptr) { // 表示插入操作
++elems_;
if (elems_ > length_) { // 数据节点超过
Resize();
}
}
return old;
}
// 链表扩容
void Resize() {
uint32_t new_length = 4; // 默认 4 个
while (new_length < elems_) { // 如果元素超过 4个, 则向上 *2 对齐
new_length *= 2;
}
LRUHandle** new_list = new LRUHandle*[new_length]; // 二维指针
// 初始化 new_list -> nullptr
memset(new_list, 0, sizeof(new_list[0]) * new_length);
uint32_t count = 0;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < length_; i++) {
// 遍历当前的 list_
LRUHandle* h = list_[i];
while (h != nullptr) {
LRUHandle* next = h->next_hash; // 获取当前节点指向的下一个节点
// 重新计算当前节点应该挂载哪一个链上
uint32_t hash = h->hash;
LRUHandle** ptr = &new_list[hash & (new_length - 1)];
// 放置在链的首部
h->next_hash = *ptr;
*ptr = h;
h = next;
count++;
}
}
// 清理旧的hash数组
assert(elems_ == count);
delete[] list_;
list_ = new_list;
length_ = new_length;
}
如果当前元素处于使用状态,则元素位于in_use_中。in_use_的数据不会从缓存中被清理。
只有元素不被外部任何地方引用,则数据将进入lru_双向链表中,新到的元素会插入到lru_链表最后。当资源不够时从lru_链表起始位置开始移出资源,直到满足资源请求。
每个部分的 Block 的数据读取过程
IndexBlock, MetaIndexBlock,DataBlock 的数据解析都是通过 Block::Iter, 它通过 二分查找 ,快速定位key, 并获取Value.
它首先对所有的重启点进行二分查找,定位到所在的重启位置,然后遍历查询精确查找 Key,Value.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
void Seek(const Slice& target) override {
uint32_t left = 0; // 偏移点下限
uint32_t right = num_restarts_ - 1; // 偏移点上限
int current_key_compare = 0;
if (Valid()) {
// 表示存在有效数据, 利用上次查询加速这次数据查询过程
current_key_compare = Compare(key_, target);
if (current_key_compare < 0) {
left = restart_index_;
} else if (current_key_compare > 0) {
right = restart_index_;
} else {
return;
}
}
// 基于重启点的二分查找,定位重启位置
while (left < right) {
uint32_t mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
uint32_t region_offset = GetRestartPoint(mid);
uint32_t shared, non_shared, value_length;
// 获取 data[mid] 的 block 的首 key
const char* key_ptr = DecodeEntry(data_ + region_offset, data_ + restarts_, &shared, &non_shared, &value_length);
if (key_ptr == nullptr || (shared != 0)) {
CorruptionError();
return;
}
Slice mid_key(key_ptr, non_shared);
if (Compare(mid_key, target) < 0) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
assert(current_key_compare == 0 || Valid());
bool skip_seek = left == restart_index_ && current_key_compare < 0;
if (!skip_seek) {
SeekToRestartPoint(left);
}
// 定位到重启点以后迭代查询每一个key,进行查询
while (true) {
if (!ParseNextKey()) {
return;
}
if (Compare(key_, target) >= 0) {
return;
}
}
}
整个数据块(IndexBlock, MetaIndexBlock或某个DataBlock) 首先通过已知的偏移位置通过 RandomAccessFile 从文件读取到内存中,形成一个 BlockContents, 它主要是将序列化的数据流读取到内存中形成的一个字节数组。
而后基于数据块的数据结构, 我们封装了这个 Block 类, 用来解析并查询这个数据块。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
/***
* 从文件中读取一个 Block 并 填充到 BlockContents 中
*
* @param file sst 文件
* @param options 文件读取选项
* @param handle Block 的偏移元信息
* @param result 将Block 转换为一个 BlockContests
*/
Status ReadBlock(RandomAccessFile* file, const ReadOptions& options, const BlockHandle& handle, BlockContents* result) {
result->data = Slice();
result->cachable = false;
result->heap_allocated = false;
// kBlockTrailerSize 是 压缩标识 + crc校验
size_t n = static_cast<size_t>(handle.size());
char* buf = new char[n + kBlockTrailerSize];
Slice contents;
Status s = file->Read(handle.offset(), n + kBlockTrailerSize, &contents, buf);
if (!s.ok()) {
delete[] buf;
return s;
}
if (contents.size() != n + kBlockTrailerSize) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("truncated block read");
}
const char* data = contents.data();
// 数据体的校验
if (options.verify_checksums) {
const uint32_t crc = crc32c::Unmask(DecodeFixed32(data + n + 1));
const uint32_t actual = crc32c::Value(data, n + 1);
if (actual != crc) {
delete[] buf;
s = Status::Corruption("block checksum mismatch");
return s;
}
}
// 获取压缩类型,如果存在压缩, 变执行压缩操作
switch (data[n]) {
case kNoCompression:
if (data != buf) {
delete[] buf;
result->data = Slice(data, n);
result->heap_allocated = false;
result->cachable = false; // Do not double-cache
} else {
result->data = Slice(buf, n);
result->heap_allocated = true;
result->cachable = true;
}
break;
case kSnappyCompression: {
size_t ulength = 0;
if (!port::Snappy_GetUncompressedLength(data, n, &ulength)) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted compressed block contents");
}
char* ubuf = new char[ulength];
if (!port::Snappy_Uncompress(data, n, ubuf)) {
delete[] buf;
delete[] ubuf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted compressed block contents");
}
delete[] buf;
result->data = Slice(ubuf, ulength);
result->heap_allocated = true;
result->cachable = true;
break;
}
default:
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("bad block type");
}
return Status::OK();
}
/***
* BlockContext 到 Block 的转换
*/
Block::Block(const BlockContents& contents)
: data_(contents.data.data()),
size_(contents.data.size()),
owned_(contents.heap_allocated) {
if (size_ < sizeof(uint32_t)) {
size_ = 0; // Error marker
} else {
// 模糊计算最多有多少个重启点
size_t max_restarts_allowed = (size_ - sizeof(uint32_t)) / sizeof(uint32_t);
if (NumRestarts() > max_restarts_allowed) {
// The size is too small for NumRestarts()
size_ = 0;
} else {
restart_offset_ = size_ - (1 + NumRestarts()) * sizeof(uint32_t);
}
}
}
Table
SST 的读取主要通过 Table 类来完成, 它内部提供了 InternalGet 方法在这个SST上进行查询用户请求的key:
Status InternalGet(const ReadOptions&, const Slice& key, void* arg, void (*handle_result)(void* arg, const Slice& k, const Slice& v))
它的查询过程
- 查询 IndexBlock 找到所有的 DataBlock的位置信息
- 对于每个要查询的DataBlock,首先使用
BloomFilter(位于FilterBlock)判断这个数据是否在这个DataBlock中。 - 如果判断数据存在, 然后加载这个DataBlock, 使用
Block来二分查找这个key.
说明 :
DataBlock 的加载过程维护了一个 LRU 的缓存机制, 对于要加载的DataBlock, Table 首先要去缓存中查看这个Block是否存在,如果不存在,则从文件中读取,并且加载到缓存中,以便于后续的读取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
/***
* 基于回调的方式, 查找某个 key, 如果找到则调用 handle_result(arg, key, value)
*
* @param options 配置选项
* @param k key
* @param arg 参数
* @param handle_result 找到外部数据时候触发的外部调用
*
*/
Status Table::InternalGet(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& k, void* arg, void (*handle_result)(void*, const Slice&,const Slice&)) {
Status s;
// IndexBlock 迭代器
Iterator* iiter = rep_->index_block->NewIterator(rep_->options.comparator);
iiter->Seek(k); // key_ >= k
if (iiter->Valid()) { // 找到这个数据
Slice handle_value = iiter->value(); // 定位到 datablock 的位置
FilterBlockReader* filter = rep_->filter; // 获得过滤器
BlockHandle handle;
// 使用 Bloom 过滤器判断一下数据是否在这个 block 里面
if (filter != nullptr && handle.DecodeFrom(&handle_value).ok() && !filter->KeyMayMatch(handle.offset(), k)) {
// Bloom 过滤器没有找到这个数据
} else {
// 加载这个 block
Iterator* block_iter = BlockReader(this, options, iiter->value());
block_iter->Seek(k);
if (block_iter->Valid()) {
// 找到这个数据,调用回调函数
(*handle_result)(arg, block_iter->key(), block_iter->value());
}
s = block_iter->status();
delete block_iter;
}
}
if (s.ok()) {
s = iiter->status();
}
delete iiter;
return s;
}