Spark 源码 | MemoryManager 解读
概述
Apache Spark 的内存管理是其高性能的核心组件之一。本文将深入分析 Spark 3.3.1 中的内存管理架构,包括 MemoryManager、MemoryPool 以及相关组件的设计原理和实现细节。
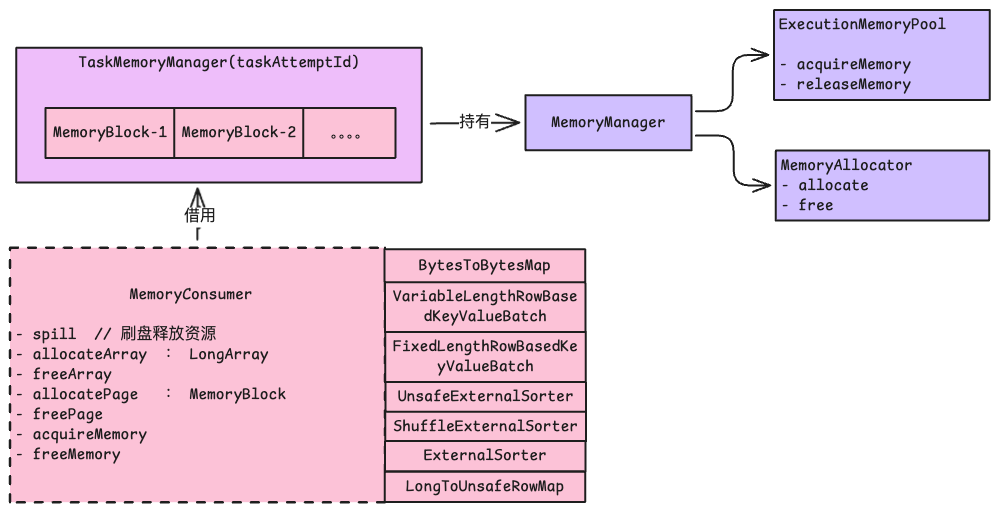
内存管理架构概览
核心组件关系图
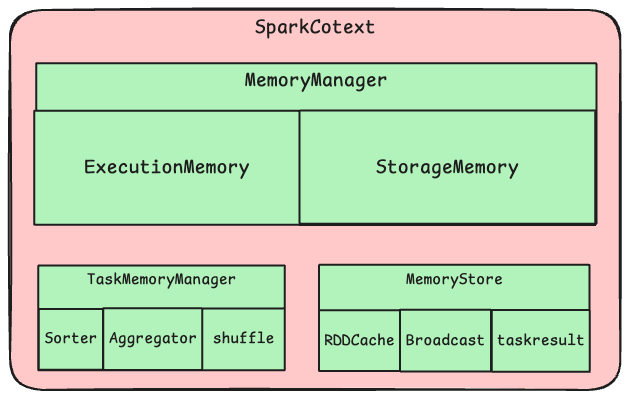
Spark 将内存分为两大类:
- 执行内存 (ExecutionMemory):用于 shuffle、join、sort、aggregation 等计算操作
- 存储内存 (StorageMemory):用于缓存 RDD、DataFrame 和广播变量
每种内存又分为:
- 堆内内存 (On-Heap):JVM 堆内存
- 堆外内存 (Off-Heap):使用 sun.misc.Unsafe 直接分配的内存
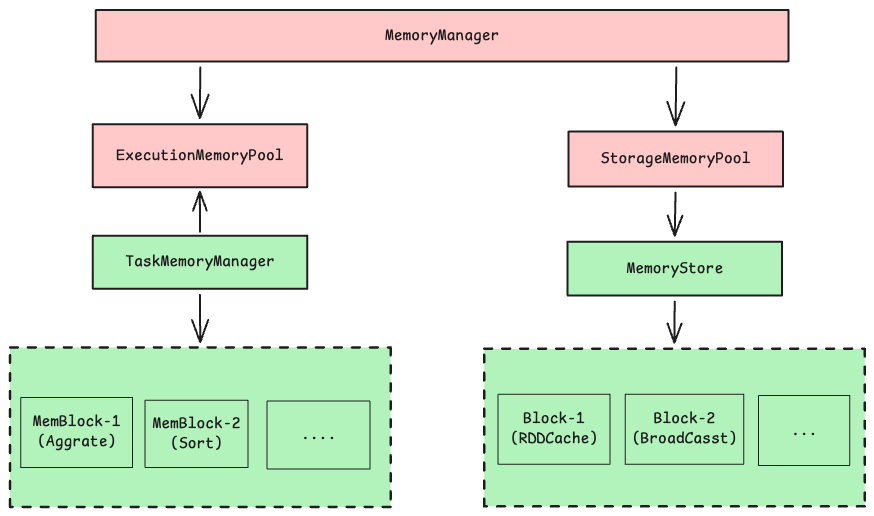
TaskMemoryManager 通过 MemoryManager 来申请使用执行内存 ExecutionMemory
MemoryStore 通过 MemoryManager 来申请使用存储内存 StorageMemory 与 展开内存 UnrollMemory(存储内存的一种)
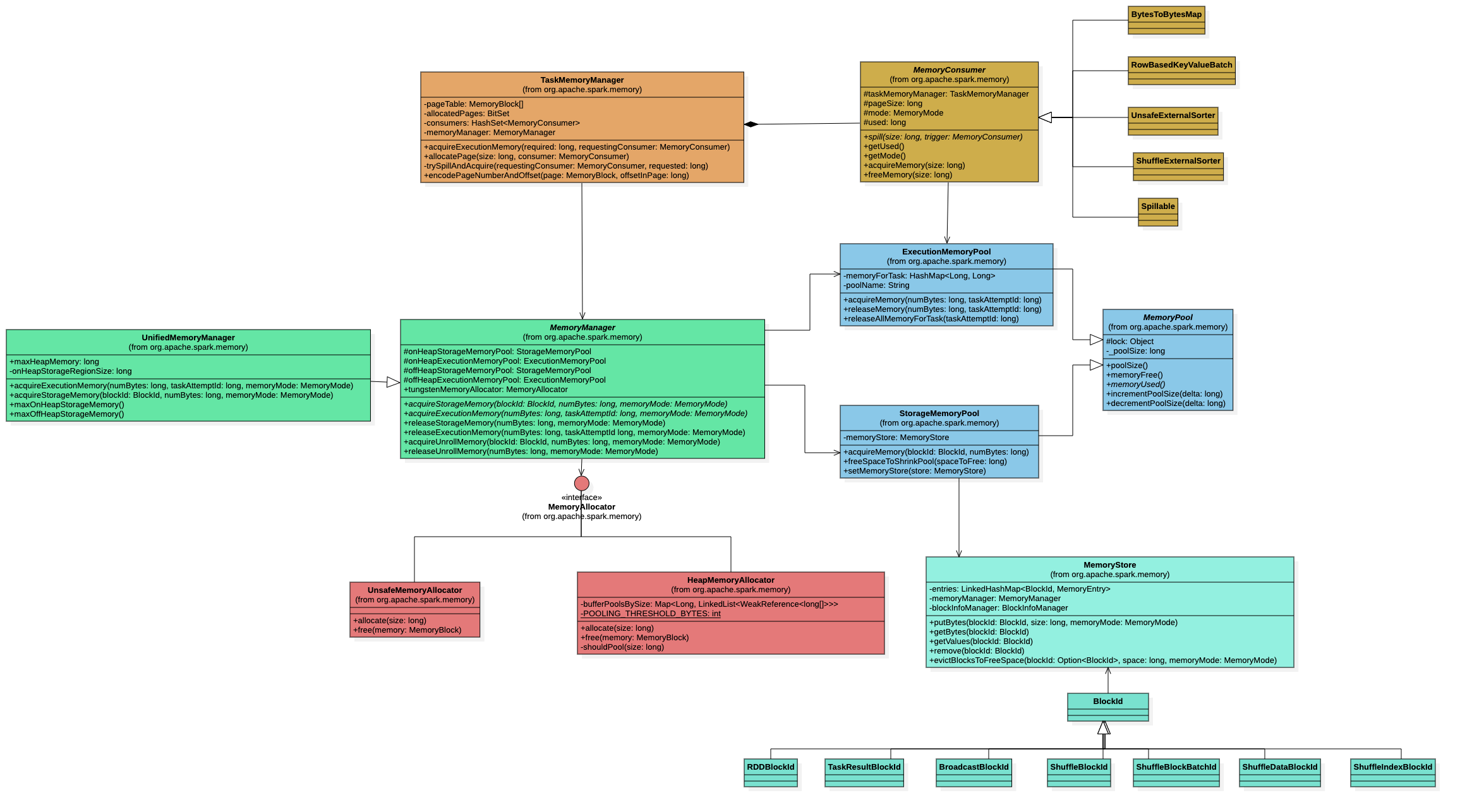
MemoryManager
类层次结构
- 内存池管理:维护四个内存池
onHeapStorageMemoryPool: 堆内存储池offHeapStorageMemoryPool: 堆外存s储池onHeapExecutionMemoryPool: 堆内执行池offHeapExecutionMemoryPool: 堆外执行池
- 内存分配接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// 获取存储内存
def acquireStorageMemory(blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Boolean
// 获取执行内存
def acquireExecutionMemory(numBytes: Long, taskAttemptId: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Long
// 释放内存
def releaseStorageMemory(numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit
def releaseExecutionMemory(numBytes: Long, taskAttemptId: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit
// 获取展开内存(用于展开iterator类型数据)
def acquireUnrollMemory(blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Boolean
// 释放展开内存
def releaseUnrollMemory(numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Unit
- Tungsten 内存管理:
他主要通过MemoryAllocator用来进行实际的内存页块分配动作, 这个 MemoryAllocator 是给执行内存(ExecutionMemory)使用, 他通过分配内存页提供给执行内存存放数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 内存模式:ON_HEAP 或 OFF_HEAP
final val tungstenMemoryMode: MemoryMode
// 页面大小计算(考虑 G1GC 优化)
val pageSizeBytes: Long = conf.get(BUFFER_PAGESIZE).getOrElse(defaultPageSizeBytes)
// 内存分配器
private[memory] final val tungstenMemoryAllocator: MemoryAllocator
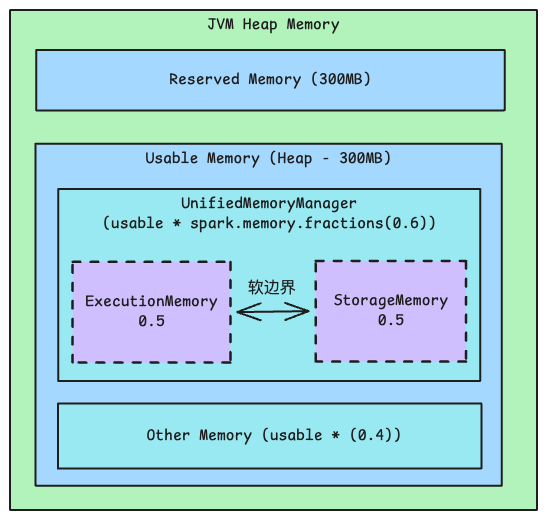
UnifiedMemoryManager 统一内存管理
UnifiedMemoryManager 是 Spark 当前使用的内存管理器,实现了执行内存和存储内存之间的软边界,允许两者互相借用内存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
// 系统保留内存
private val RESERVED_SYSTEM_MEMORY_BYTES = 300 * 1024 * 1024 // 300MB
// 内存分数配置
spark.memory.fraction = 0.6 // Spark 可用内存占比
spark.memory.storageFraction = 0.5 // 存储内存在 Spark 内存中的占比
内存借用机制
执行内存借用存储内存:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
override private[memory] def acquireExecutionMemory(
numBytes: Long, taskAttemptId: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Long = {
// 尝试从 StoragePool 内部获取一定数量的内存分配给 ExecutionPool
// 获取数量 min(当前请求的Execution内存值, max(当前存储剩余内存, 当前存储超用Execution的部分内存))
def maybeGrowExecutionPool(extraMemoryNeeded: Long): Unit = {
if (extraMemoryNeeded > 0) {
// 计算可从存储池回收的内存
val memoryReclaimableFromStorage = math.max(
storagePool.memoryFree, // 存储池空闲内存
storagePool.poolSize - storageRegionSize) // 存储池借用的执行内存 {storageRegionSize:存储侧的基准内存大小(UserMemory*0.5)}
if (memoryReclaimableFromStorage > 0) {
val spaceToReclaim = storagePool.freeSpaceToShrinkPool(
math.min(extraMemoryNeeded, memoryReclaimableFromStorage))
storagePool.decrementPoolSize(spaceToReclaim)
executionPool.incrementPoolSize(spaceToReclaim)
}
}
}
// 当前 Execution 能使用的最大内存 : 总内存 - min(StoragePool当前使用内存,StoragePool标准可用内存)
def computeMaxExecutionPoolSize(): Long = {
maxMemory - math.min(storagePool.memoryUsed, storageRegionSize)
}
executionPool.acquireMemory(numBytes, taskAttemptId, maybeGrowExecutionPool, computeMaxPoolSize)
}
存储内存借用执行内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
override def acquireStorageMemory( blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long, memoryMode: MemoryMode): Boolean = {
// 如果存储内存资源不足, 则需要从 Execution申请内存 : min(ExecutionPool剩余内存, 当前不足的内存差额)
if (numBytes > storagePool.memoryFree) {
// 从执行池借用空闲内存
val memoryBorrowedFromExecution = Math.min(executionPool.memoryFree, numBytes - storagePool.memoryFree)
executionPool.decrementPoolSize(memoryBorrowedFromExecution)
storagePool.incrementPoolSize(memoryBorrowedFromExecution)
}
storagePool.acquireMemory(blockId, numBytes)
}
ExecutionMemoryPool 执行内存池
公平性保证机制
ExecutionMemoryPool 实现了任务间的公平内存分配:
- 最小保证:每个任务至少获得
1/(2N)的内存 - 最大限制:每个任务最多获得
1/N的内存 - N:当前活跃任务数
内存分配算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
def acquireMemory(numBytes: Long, taskAttemptId: Long,
maybeGrowPool: Long => Unit,
computeMaxPoolSize: () => Long): Long = {
while (true) {
val numActiveTasks = memoryForTask.keys.size
val curMem = memoryForTask(taskAttemptId)
// 如果当前 ExecutionPool 的剩余内存不满足内存需求, 则尝试从 StoragePool 中获取差额内存
maybeGrowPool(numBytes - memoryFree)
val maxPoolSize = computeMaxPoolSize()
val maxMemoryPerTask = maxPoolSize / numActiveTasks // 1/N
val minMemoryPerTask = poolSize / (2 * numActiveTasks) // 1/(2N)
// 计算可分配内存
val maxToGrant = math.min(numBytes, math.max(0, maxMemoryPerTask - curMem))
val toGrant = math.min(maxToGrant, memoryFree)
// 分配决策
if (toGrant < numBytes && curMem + toGrant < minMemoryPerTask) {
// 内存不足且未达到最小保证,等待
lock.wait()
} else {
// 分配内存
memoryForTask(taskAttemptId) += toGrant
return toGrant
}
}
}
内存分配示例
假设有 3 个任务,总池大小 600MB:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
初始状态:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ExecutionMemoryPool (600MB) │
│ ┌─────────────┬─────────────┬─────────────┬─────────────┐ │
│ │ Task A │ Task B │ Task C │ Free │ │
│ │ 150MB │ 100MB │ 50MB │ 300MB │ │
│ │ 最大: 200MB │ 最大: 200MB │ 最大: 200MB │ │ │
│ │ 最小: 100MB │ 最小: 100MB │ 最小: 100MB │ │ │
│ └─────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Task D 加入后:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ExecutionMemoryPool (600MB) │
│ ┌─────────┬─────────┬─────────┬──────────┬─────────────┐ │
│ │ Task A │ Task B │ Task C │ Task D │ Free │ │
│ │ 150MB │ 100MB │ 50MB │ 0MB │ 300MB │ │
│ │最大:150MB│最大:150MB│最大:150MB│最大:150MB│ │ │
│ │最小: 75MB│最小: 75MB│最小: 75MB│最小: 75MB│ │ │
│ └─────────┴─────────┴─────────┴──────────┴─────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
StorageMemoryPool 存储内存池
核心功能
- 缓存管理:管理 RDD、DataFrame 的缓存
- 块驱逐:内存不足时驱逐 LRU 块
- Unroll 支持:支持迭代器展开操作
内存分配流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def acquireMemory(blockId: BlockId, numBytes: Long): Boolean = {
val numBytesToFree = math.max(0, numBytes - memoryFree)
if (numBytesToFree > 0) {
// 驱逐块以释放内存
memoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace(Some(blockId), numBytesToFree, memoryMode)
}
val enoughMemory = numBytes <= memoryFree
if (enoughMemory) {
_memoryUsed += numBytes
}
enoughMemory
}
块驱逐策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def freeSpaceToShrinkPool(spaceToFree: Long): Long = {
// 1. 首先释放未使用的内存
val spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory = math.min(spaceToFree, memoryFree)
val remainingSpaceToFree = spaceToFree - spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory
// 2. 如果还需要更多空间,驱逐缓存块
if (remainingSpaceToFree > 0) {
val spaceFreedByEviction = memoryStore.evictBlocksToFreeSpace(
None, remainingSpaceToFree, memoryMode)
spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory + spaceFreedByEviction
} else {
spaceFreedByReleasingUnusedMemory
}
}
TaskMemoryManager 任务级内存管理
TaskMemoryManager 为单个任务提供内存管理服务:
- 页表管理:管理 Tungsten 内存页
- 地址编码:将 64 位地址编码为页号+偏移量
- 消费者管理:管理任务内的内存消费者
- 溢出协调:协调内存不足时的溢出操作
地址编码方案
1
2
3
private static final int PAGE_NUMBER_BITS = 13; // 页号位数:13 位,支持 8192 个页面
static final int OFFSET_BITS = 64 - PAGE_NUMBER_BITS; // 偏移量位数:51 位
public static final long MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES = ((1L << 31) - 1) * 8L; // 最大页面大小:约 17GB
地址编码格式:
1
2
3
┌─────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 页号(13位) │ 偏移量(51位) │
└─────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
内存分配策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
/**
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ TaskMemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ 参数验证 │
│ required >= 0 │
│ consumer != null│
└─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ 获取模式 │
│ mode = consumer │
│ .getMode() │
└─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ 同步代码块 │
│ synchronized │
└─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 第一次尝试获取内存 │
│ got = memoryManager │
│ .acquireExecutionMemory( │
│ required, taskAttemptId, mode) │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ got < req? │
└─────────────┘
│ │
Yes No
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 内存不足 │ │ 内存充足 │
│ 需要溢出 │ │ 直接返回 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 构建消费者映射 │ │ consumers.add() │
│ TreeMap<Long,List<Consumer>>│ │ return got │
│ 按内存使用量排序 │ └─────────────────┘
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ 溢出循环 │
│ while(got < required && │
│ !sortedConsumers.isEmpty) │
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ 选择溢出目标 │
│ ceilingEntry(required-got) │
│ 或 lastEntry() 如果没找到 │
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ trySpillAndAcquire │
│ 尝试溢出并获取释放的内存 │
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ 溢出子流程 │
│ consumerToSpill.spill() │
│ memoryManager.acquire...() │
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ 更新got,继续循环 │
│ 直到满足需求或无消费者 │
└─────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ 添加消费者到集合 │
│ consumers.add(consumer) │
│ 返回获取的内存 │
└─────────────────────────────┘
*/
public long acquireExecutionMemory(long required, MemoryConsumer requestingConsumer) {
MemoryMode mode = requestingConsumer.getMode();
synchronized (this) {
long got = memoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory(required, taskAttemptId, mode);
if (got < required) {
// 构建消费者优先级队列(按内存使用量排序)
TreeMap<Long, List<MemoryConsumer>> sortedConsumers = new TreeMap<>();
for (MemoryConsumer c: consumers) {
if (c.getUsed() > 0 && c.getMode() == mode) {
long key = c == requestingConsumer ? 0 : c.getUsed();
sortedConsumers.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(c);
}
}
// 迭代溢出消费者直到获得足够内存
while (got < required && !sortedConsumers.isEmpty()) {
// 选择内存使用量 >= 剩余需求的最小消费者
Map.Entry<Long, List<MemoryConsumer>> currentEntry =
sortedConsumers.ceilingEntry(required - got);
// 如果没有足够大的消费者,选择最大的
if (currentEntry == null) {
currentEntry = sortedConsumers.lastEntry();
}
List<MemoryConsumer> cList = currentEntry.getValue();
got += trySpillAndAcquire(requestingConsumer, required - got, cList, cList.size() - 1);
if (cList.isEmpty()) {
sortedConsumers.remove(currentEntry.getKey());
}
}
}
consumers.add(requestingConsumer);
return got;
}
}
MemoryConsumer
MemoryConsumer 是Spark内存管理系统中的抽象基类,代表一个可以消费内存并支持溢出的组件
内存申请与释放 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ acquireMemory(size) → 申请内存 │
│ freeMemory(size) → 释放内存 │
│ allocatePage(size) → 分配页面 │
│ freePage(page) → 释放页面 │
│ allocateArray(size) → 分配长整型数组 │
│ freeArray(array) → 释放数组 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
溢出机制 (核心抽象方法) :
1
2
3
4
5
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ spill(size, trigger) → 抽象方法 │
│ 子类必须实现具体的溢出逻辑 │
│ 将内存中的数据写入磁盘以释放内存 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
状态跟踪 :
1
2
3
4
5
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ used → 当前使用的内存大小 │
│ getUsed() → 获取使用量 │
│ getMode() → 获取内存模式(堆内/堆外) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
主要实现的类 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
🔄 ShuffleExternalSorter
└── Shuffle过程中的外部排序器,当内存不足时将数据溢出到磁盘
🔄 UnsafeExternalSorter
└── 基于Unsafe的外部排序器,用于高性能排序操作
🔄 BytesToBytesMap
└── 字节到字节的映射表,用于聚合操作
🔄 RowBasedKeyValueBatch
└── 基于行的键值批处理,用于SQL执行
内存分配流程 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ Consumer.acquireMemory(100MB) │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ TaskMemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory() │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ MemoryManager.acquireExecutionMemory() │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ 如果内存不足,选择其他Consumer进行溢出 │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ selectedConsumer.spill(size, requestingConsumer) │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ 释放内存后重新尝试分配 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权