Spark 源码 | RPC 篇
本文通过阅读 Spark RPC 相关部分的代码,了解学习 spark RPC 的架构实现以及原理和细节。
参考的 spark 版本为 2.3.1.
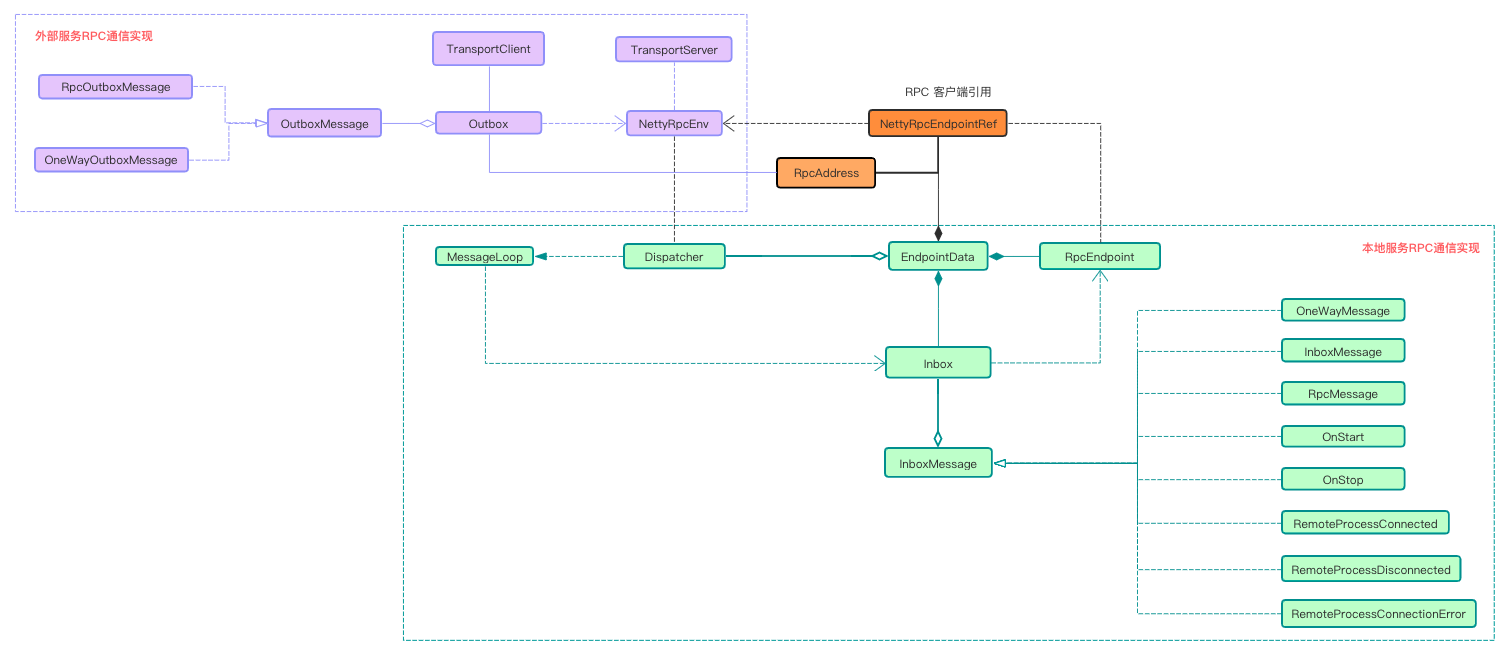
spark RPC 在实现上主要分为本地RPC与远程RPC通信。 本地 RPC 通信主要是以线程实现的异步通信方式,而远程RPC通信主要以netty实现的socket通信方式。
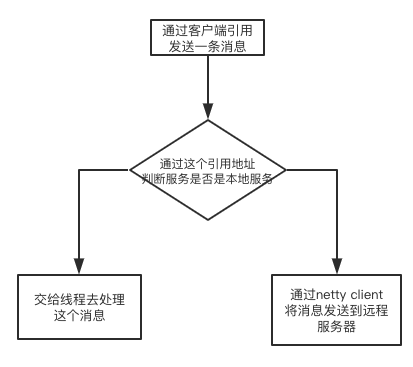
如下所示, NettyRpcEndpointRef 为RPC通信的客户端引用,每一个 NettyRpcEndpointRef会包含一个RpcAddress记录这个引用的通信对方地址。
通过 NettyRpcEndpointRef 发送的消息最终会通过NettyRpcEnv来负责处理发送, 它提供过比对 RpcAddress 是否为标志地址,来判断这个是一个本地消息还是远程消息。 然后交给相应的处理组件来处理。
说明:
RpcEndpoint为本地服务的接收端, 每一个本地的RpcEndponit都有一个对应的NettyRpcEndpointRef.Inbox与Outbox是NettyRpcEndpointRef对应的最终消息发送工具, 不一样的是Inbox为内部服务的消息发送工具而Outbox为外部消息发送工具。- 内部
NettyRpcEndpointRef发送通过Dispatcher来中转发送到指定的实现类。
有关具体的细节可以阅读 spark-2.3.1/core/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/rpc at master · Aiden-Dong/spark-2.3.1 · GitHub
内部 RPC
内部 RPC 通过 Dispatcher 来实现分发的。
我们通过 NettyRpcEndpointRef 的客户端引用发送消息时,会将消息封装成 RequestMessage 转交给 NettyRpcEnv.
1
2
3
4
override def send(message: Any): Unit = {
require(message != null, "Message is null")
nettyEnv.send(new RequestMessage(nettyEnv.address, this, message))
}
在NettyRpcEnv中会比对接受者的地址(RequestMessage 的第二个参数中),如果是本地服务地址, 则将消息转交给 Dispatcher.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
private[netty] def send(message: RequestMessage): Unit = {
val remoteAddr = message.receiver.address
if (remoteAddr == address) {
// Message to a local RPC endpoint.
try {
dispatcher.postOneWayMessage(message)
} catch {
case e: RpcEnvStoppedException => logDebug(e.getMessage)
}
} else {
// Message to a remote RPC endpoint.
postToOutbox(message.receiver, OneWayOutboxMessage(message.serialize(this)))
}
}
Dispatcher
Dispatcher 中重要的成员变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
private val endpoints: ConcurrentMap[String, EndpointData] = new ConcurrentHashMap[String, EndpointData] // 所有的 EndpointData 映射集合
private val endpointRefs: ConcurrentMap[RpcEndpoint, RpcEndpointRef] = new ConcurrentHashMap[RpcEndpoint, RpcEndpointRef] // 所有的 RpcEndpoint->RpcEndpointRef 映射关系
// Track the receivers whose inboxes may contain messages.
private val receivers = new LinkedBlockingQueue[EndpointData] // 有待处理消息的 EndpointData 阻塞列表
private val threadpool: ThreadPoolExecutor // 轮训 receivers 的线程池
Dispatcher 是一个本地RPC的消息路由服务。 它维护这本地的 NettyRpcEndpointRef 到 RpcEndpoint 的一个映射关系。
当创建一个 RpcEndpoint 时, 需要调用 registerRpcEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint), 这个是被封装到 NettyRpcEnv 中。
所以我们看到的是诸如这种的注册过程:
1
2
val executorEndpoint = new LocalEndpoint(rpcEnv, userClassPath, scheduler, this, totalCores)
localEndpoint = rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("LocalSchedulerBackendEndpoint", executorEndpoint)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def registerRpcEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint): NettyRpcEndpointRef = {
val addr = RpcEndpointAddress(nettyEnv.address, name)
val endpointRef = new NettyRpcEndpointRef(nettyEnv.conf, addr, nettyEnv)
synchronized {
if (stopped) {
throw new IllegalStateException("RpcEnv has been stopped")
}
// 存放 name -> EndpointData 的映射关系
if (endpoints.putIfAbsent(name, new EndpointData(name, endpoint, endpointRef)) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"There is already an RpcEndpoint called $name")
}
val data = endpoints.get(name)
endpointRefs.put(data.endpoint, data.ref)
// 触发 OnStart 消息
receivers.offer(data)
}
endpointRef
}
EndpointData 中维护这 NettyRpcEndpointRef, RpcEndpoint 以及 Inbox 的信息。 Dispatcher 使用 endpoints 维护所有的 EndpointData. 我们可以通过 NettyRpcEndpointRef 的 name 属性从 endpoints 找到对应的EndpointData信息。
Dispatcher 中使用 receivers 阻塞队列来保存有待处理消息的 EndpointData。
当使用 Dispatcher 分发消息时, Dispatcher 首先将消息存放到对应的 Inbox 中, 然后将其EndpointData压入到 receivers中等待获取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
private def postMessage(
...
data.inbox.post(message)
receivers.offer(data)
...
}
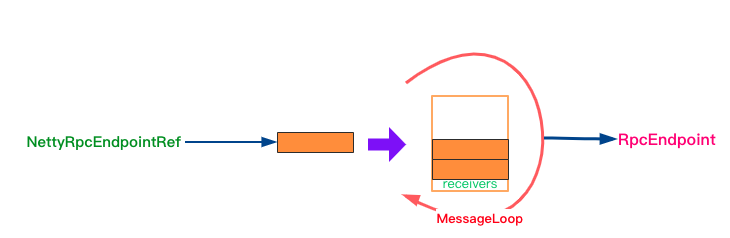
MessageLoop
Dispatcher 内部线程实现, 负责获取 receivers 中的阻塞消息并对应的 RpcEndpoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
private class MessageLoop extends Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (true) {
try {
val data = receivers.take()
if (data == PoisonPill) {
// Put PoisonPill back so that other MessageLoops can see it.
receivers.offer(PoisonPill)
return
}
data.inbox.process(Dispatcher.this)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) => logError(e.getMessage, e)
}
}
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // exit
}
}
}
RpcEndpoint
RpcEndpoint 是一个本地化的服务实体类。 它异步接受消息并进行处理。
RpcEndpoint 的生命周期为 constructor -> onStart -> receive* -> onStop ,如果 RpcEndpoint 抛出了错误, RpcEndpoint 就会调用 onError 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
def onStart(): Unit = {
// By default, do nothing.
}
def onStop(): Unit = {
// By default, do nothing.
}
def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case _ => throw new SparkException(self + " does not implement 'receive'")
}
def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case _ => context.sendFailure(new SparkException(self + " won't reply anything"))
}
def onError(cause: Throwable): Unit = {
// By default, throw e and let RpcEnv handle it
throw cause
}
Inbox
Inbox 是内部服务的消息发送实现, 当有消息到达时, Inbox 被 MessageLoop 用线程的方式触发.
它轮训获取所有被放到这个Inbox 中的消息, 并调用 RpcEndpoint 去匹配消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
message match {
case RpcMessage(_sender, content, context) =>
endpoint.receiveAndReply(context).applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>...})
case OneWayMessage(_sender, content) =>
endpoint.receive.applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg => ...})
case OnStart =>
endpoint.onStart()
case OnStop =>
endpoint.onStop()
case RemoteProcessConnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onConnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessDisconnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onDisconnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessConnectionError(cause, remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onNetworkError(cause, remoteAddress)
}
}
外部 RPC
如果发现在调用 send 时发现地址是外部地址, 则消息为外部消息, 需要通过 Outbox 发送出去。
逻辑大致如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private def postToOutbox(receiver: NettyRpcEndpointRef, message: OutboxMessage): Unit = {
val targetOutbox = {
val outbox = outboxes.get(receiver.address)
if (outbox == null) {
val newOutbox = new Outbox(this, receiver.address)
val oldOutbox = outboxes.putIfAbsent(receiver.address, newOutbox)
if (oldOutbox == null) {
newOutbox
} else {
oldOutbox
}
} else {
outbox
}
}
targetOutbox.send(message)
}
Outbox 通过 netty 实现的TransportClient 将消息发送出去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private def drainOutbox(): Unit = {
var message: OutboxMessage = messages.poll()
while (true) {
message.sendWith(client)
message = messages.poll()
if (message == null) {
return
}
}
}
}
RPC 实现
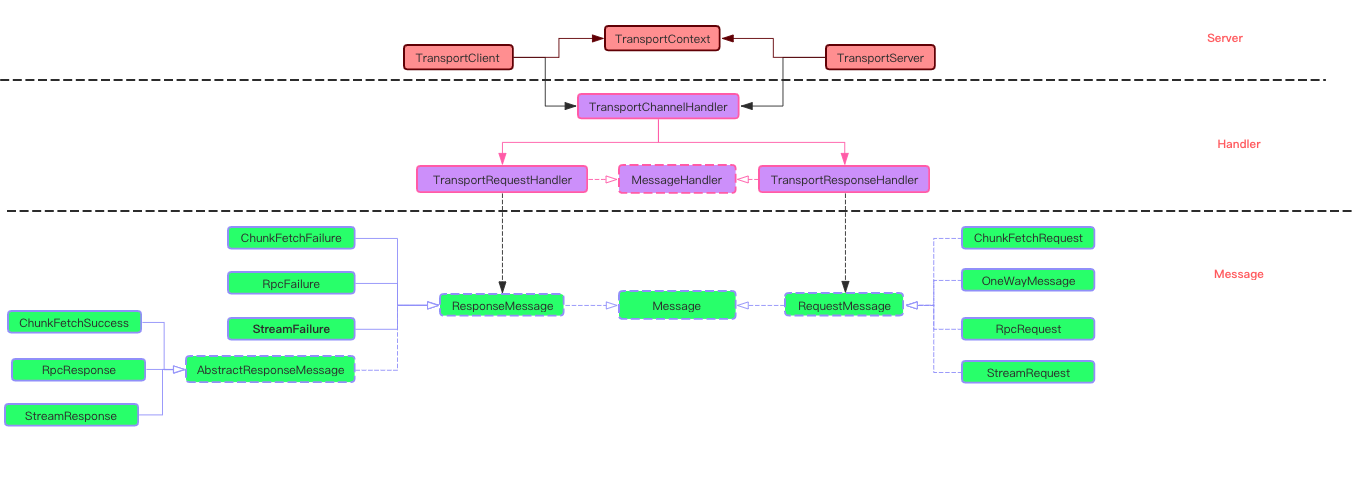
TransportClient 与 TransportServer 是 spark 远程rpc 通信的客户端与服务器类实现。 他们内部使用的Netty框架。
TransportClient 的建立方式为 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.channel(socketChannelClass)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // 关闭 Nagle 算法,允许发送小包
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 保活探测
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, conf.connectionTimeoutMs()) // 超时
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, pooledAllocator);
if (conf.receiveBuf() > 0) {
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, conf.receiveBuf()); // 接受缓冲区大小
}
if (conf.sendBuf() > 0) {
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, conf.sendBuf()); // 发送缓冲区大小
}
final AtomicReference<TransportClient> clientRef = new AtomicReference<>();
final AtomicReference<Channel> channelRef = new AtomicReference<>();
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
TransportChannelHandler clientHandler = context.initializePipeline(ch);
clientRef.set(clientHandler.getClient());
channelRef.set(ch);
}
});
功能接口主要为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class TransportClient implements Closeable {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransportClient.class);
private final Channel channel; // netty client channel
private final TransportResponseHandler handler;
@Nullable private String clientId;
private volatile boolean timedOut;
public TransportClient(Channel channel, TransportResponseHandler handler) {
this.channel = Preconditions.checkNotNull(channel);
this.handler = Preconditions.checkNotNull(handler);
this.timedOut = false;
}
// 获取单个块数据
public void fetchChunk(long streamId, int chunkIndex, ChunkReceivedCallback callback) { ...}
// 获取流数据
public void stream(String streamId, StreamCallback callback) { ... }
// 发送一个rpc请求
public long sendRpc(ByteBuffer message, RpcResponseCallback callback) { ... }
// prc 请求的同步实现
public ByteBuffer sendRpcSync(ByteBuffer message, long timeoutMs) { ... }
// 发送一个不需要响应的消息。
public void send(ByteBuffer message) { ... }
...
}
TransportServer 的建立方式为 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NettyUtils.getServerChannelClass(ioMode)) // NIO or EPOll
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, allocator)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, allocator);
this.metrics = new NettyMemoryMetrics(
allocator, conf.getModuleName() + "-server", conf);
if (conf.backLog() > 0) {
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, conf.backLog()); // listen 半链接长度
}
if (conf.receiveBuf() > 0) {
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, conf.receiveBuf()); // recvbuffer
}
if (conf.sendBuf() > 0) {
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, conf.sendBuf()); // sendbuffer
}
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
RpcHandler rpcHandler = appRpcHandler;
for (TransportServerBootstrap bootstrap : bootstraps) {
rpcHandler = bootstrap.doBootstrap(ch, rpcHandler);
}
context.initializePipeline(ch, rpcHandler);
}
});
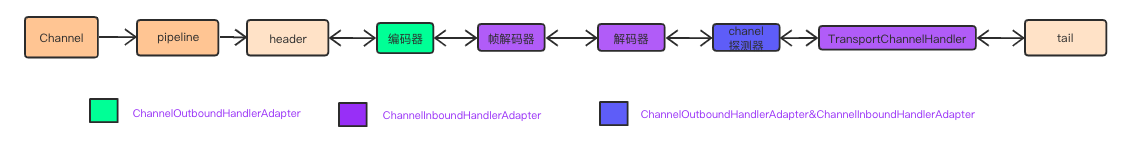
从上面可以看出 Handler 的初始化都是调用的 TransportContext.initializePipeline 完成的,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public TransportChannelHandler initializePipeline(
SocketChannel channel,
RpcHandler channelRpcHandler) {
try {
TransportChannelHandler channelHandler = createChannelHandler(channel, channelRpcHandler);
channel.pipeline()
.addLast("encoder", ENCODER) // encode -- out
.addLast(TransportFrameDecoder.HANDLER_NAME, NettyUtils.createFrameDecoder()) // 帧解码器
.addLast("decoder", DECODER) // decode
.addLast("idleStateHandler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, conf.connectionTimeoutMs() / 1000)) // 检查 channel 的活跃情况
.addLast("handler", channelHandler);
return channelHandler;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
logger.error("Error while initializing Netty pipeline", e);
throw e;
}
}
所以 client, server 具有相同的通信模型 :
消息的监听处理都是通过 TransportChannelHandler 来实现的, 双方通过 Message 来交互信息。
编解码工具用于数据流与Message的转换。保证数据在TransportChannelHandler里面是以 Message 来呈现给应用方。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object request) throws Exception {
if (request instanceof RequestMessage) {
requestHandler.handle((RequestMessage) request);
} else if (request instanceof ResponseMessage) {
responseHandler.handle((ResponseMessage) request);
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(request);
}
}
TransportChannelHandler 将会对消息进行解析, 对于 RequestMessage 将转交给 TransportRequestHandler, ResponseMessage 交给 TransportResponseHandler 处理。
这两个MessageHandler才是消息的最终解析与处理工具。
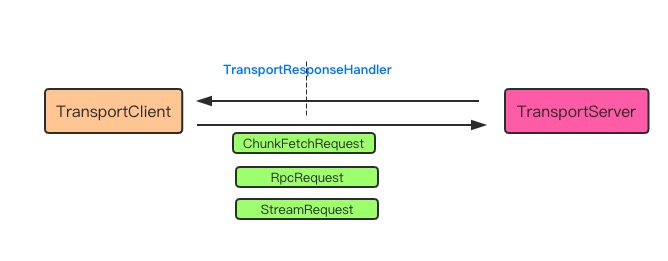
TransportResponseHandler
TransportResponseHandler 一般是与 TransportClient 相关联。 对于c/s模型, TransportClient 通过本地请求触发, 去 TransportServer 获取相关的请求如 : ChunkFetchRequest, RpcRequest, StreamRequest. 需要获取返回消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
public class TransportResponseHandler extends MessageHandler<ResponseMessage> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransportResponseHandler.class);
private final Channel channel;
/**
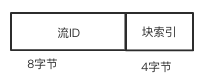
* 获取流数据块的请求处理方式集合
* 当有程序请求时, 会存储这个请求块id,以及这个块的处理回调函数, 如果块的请求返回, 则执行回调函数。
*/
private final Map<StreamChunkId, ChunkReceivedCallback> outstandingFetches;
/**
* RPC 请求处理方式
* 当有程序请求时, 会存储这个rpc请求id, 以及对这个响应的处理回调函数, 如果rpc响应, 则调用回调函数。
*/
private final Map<Long, RpcResponseCallback> outstandingRpcs;
/**
* 流的请求处理函数, 队列模型存储
*/
private final Queue<Pair<String, StreamCallback>> streamCallbacks;
private volatile boolean streamActive;
/** Records the time (in system nanoseconds) that the last fetch or RPC request was sent. */
private final AtomicLong timeOfLastRequestNs;
public TransportResponseHandler(Channel channel) {
this.channel = channel;
this.outstandingFetches = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
this.outstandingRpcs = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
this.streamCallbacks = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
this.timeOfLastRequestNs = new AtomicLong(0);
}
@Override
public void handle(ResponseMessage message) throws Exception {
if (message instanceof ChunkFetchSuccess) {
// 对于流的块请求成功响应, 则调用对这个块的回调函数。
ChunkFetchSuccess resp = (ChunkFetchSuccess) message;
ChunkReceivedCallback listener = outstandingFetches.get(resp.streamChunkId);
listener.onSuccess(resp.streamChunkId.chunkIndex, resp.body());
} else if (message instanceof ChunkFetchFailure) {
// 对于这个流的块请求失败, 调用失败处理函数
ChunkFetchFailure resp = (ChunkFetchFailure) message;
ChunkReceivedCallback listener = outstandingFetches.get(resp.streamChunkId);
listener.onFailure(resp.streamChunkId.chunkIndex, new ChunkFetchFailureException(
"Failure while fetching " + resp.streamChunkId + ": " + resp.errorString));
} else if (message instanceof RpcResponse) {
// 对于 RPC 请求的成功响应
RpcResponse resp = (RpcResponse) message;
RpcResponseCallback listener = outstandingRpcs.get(resp.requestId);
listener.onSuccess(resp.body().nioByteBuffer());
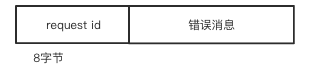
} else if (message instanceof RpcFailure) {
// 对于 RPC 请求的失败情况
RpcFailure resp = (RpcFailure) message;
RpcResponseCallback listener = outstandingRpcs.get(resp.requestId);
listener.onFailure(new RuntimeException(resp.errorString));
} else if (message instanceof StreamResponse) {
// 对于流请求的成功应答消息
StreamResponse resp = (StreamResponse) message;
Pair<String, StreamCallback> entry = streamCallbacks.poll();
StreamCallback callback = entry.getValue();
if (resp.byteCount > 0) {
StreamInterceptor interceptor = new StreamInterceptor(this, resp.streamId, resp.byteCount,callback);
TransportFrameDecoder frameDecoder = (TransportFrameDecoder) channel.pipeline().get(TransportFrameDecoder.HANDLER_NAME);
frameDecoder.setInterceptor(interceptor);
streamActive = true;
} else {
callback.onComplete(resp.streamId);
}
}
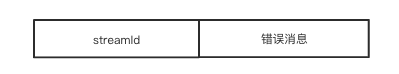
} else if (message instanceof StreamFailure) {
// 流请求失败
StreamFailure resp = (StreamFailure) message;
Pair<String, StreamCallback> entry = streamCallbacks.poll();
...
callback.onFailure(resp.streamId, new RuntimeException(resp.error));
}
}
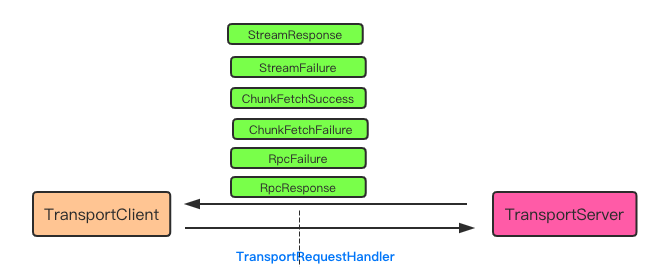
TransportRequestHandler
TransportRequestHandler 一般是与 TransportServer 相关联。 对于c/s模型, TransportServer 一般通过TransportClient 请求触发, 根据请求信息恢复如 : ChunkFetchSuccess, ChunkFetchFailure, RpcResponse, RpcFailure, StreamResponse, StreamFailure 等的消息.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
public class TransportRequestHandler extends MessageHandler<RequestMessage> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransportRequestHandler.class);
private final Channel channel; // session channel
private final TransportClient reverseClient; // session channel client
private final RpcHandler rpcHandler; // rpc handler
private final StreamManager streamManager; //
private final long maxChunksBeingTransferred;
public TransportRequestHandler(
Channel channel,
TransportClient reverseClient,
RpcHandler rpcHandler,
Long maxChunksBeingTransferred) {
this.channel = channel;
this.reverseClient = reverseClient;
this.rpcHandler = rpcHandler;
this.streamManager = rpcHandler.getStreamManager();
this.maxChunksBeingTransferred = maxChunksBeingTransferred;
}
@Override
public void handle(RequestMessage request) {
if (request instanceof ChunkFetchRequest) {
// 流数据块请求信息
processFetchRequest((ChunkFetchRequest) request);
} else if (request instanceof RpcRequest) {
// RPC 请求信息
processRpcRequest((RpcRequest) request);
} else if (request instanceof OneWayMessage) {
// 无应答 RPC 请求信息
processOneWayMessage((OneWayMessage) request);
} else if (request instanceof StreamRequest) {
// 流请求信息
processStreamRequest((StreamRequest) request);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown request type: " + request);
}
}
private void processFetchRequest(final ChunkFetchRequest req) {
// 流数据块请求信息
ManagedBuffer buf;
try {
buf = streamManager.getChunk(req.streamChunkId.streamId, req.streamChunkId.chunkIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
respond(new ChunkFetchFailure(req.streamChunkId, Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e)));
return;
}
respond(new ChunkFetchSuccess(req.streamChunkId, buf)).addListener(future -> {
streamManager.chunkSent(req.streamChunkId.streamId);
});
}
private void processStreamRequest(final StreamRequest req) {
// 流请求信息
ManagedBuffer buf;
try {
buf = streamManager.openStream(req.streamId);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(String.format("Error opening stream %s for request from %s", req.streamId, getRemoteAddress(channel)), e);
respond(new StreamFailure(req.streamId, Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e)));
return;
}
if (buf != null) {
streamManager.streamBeingSent(req.streamId);
respond(new StreamResponse(req.streamId, buf.size(), buf)).addListener(future -> {
streamManager.streamSent(req.streamId);
});
} else {
respond(new StreamFailure(req.streamId, String.format("Stream '%s' was not found.", req.streamId)));
}
}
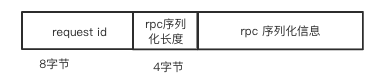
private void processRpcRequest(final RpcRequest req) {
// RPC 请求处理
try {
rpcHandler.receive(reverseClient, req.body().nioByteBuffer(), new RpcResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ByteBuffer response) {
respond(new RpcResponse(req.requestId, new NioManagedBuffer(response)));
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable e) {
respond(new RpcFailure(req.requestId, Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e)));
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while invoking RpcHandler#receive() on RPC id " + req.requestId, e);
respond(new RpcFailure(req.requestId, Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e)));
} finally {
req.body().release();
}
}
// 无需应答的 RPC 处理
private void processOneWayMessage(OneWayMessage req) {
try {
rpcHandler.receive(reverseClient, req.body().nioByteBuffer());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while invoking RpcHandler#receive() for one-way message.", e);
} finally {
req.body().release();
}
}
private ChannelFuture respond(Encodable result) {
SocketAddress remoteAddress = channel.remoteAddress();
return channel.writeAndFlush(result).addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
logger.trace("Sent result {} to client {}", result, remoteAddress);
} else {
logger.error(String.format("Error sending result %s to %s; closing connection",
result, remoteAddress), future.cause());
channel.close();
}
});
}
}
协议内容
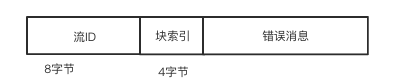
消息类型使用一个字节的值表示, 可表示范围为 : -128 ~ 127
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
case 0: return ChunkFetchRequest;
case 1: return ChunkFetchSuccess;
case 2: return ChunkFetchFailure;
case 3: return RpcRequest;
case 4: return RpcResponse;
case 5: return RpcFailure;
case 6: return StreamRequest;
case 7: return StreamResponse;
case 8: return StreamFailure;
case 9: return OneWayMessage;
case -1: throw new IllegalArgumentException("User type messages cannot be decoded.");
default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown message type: " + id);
参考内容